Article contents
Influence of surface viscosity on droplets in shear flow
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 22 February 2016
Abstract
The behaviour of a single droplet in an immiscible external fluid, submitted to shear flow is investigated using numerical simulations. The surface of the droplet is modelled by a Boussinesq–Scriven constitutive law involving the interfacial viscosities and a constant surface tension. A numerical method using Loop subdivision surfaces to represent droplet interface is introduced. This method couples boundary element method for fluid flows and finite element method to take into account the stresses due to the surface dilational and shear viscosities and surface tension. Validation of the numerical scheme with respect to previous analytic and computational work is provided, with particular attention to the viscosity contrast and the shear and dilational viscosities characterized both by a Boussinesq number 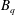 $B_{q}$. Then, influence of equal surface viscosities on steady-state characteristics of a droplet in shear flow are studied, considering both small and large deformations and for a large range of bulk viscosity contrast. We find that small deformation analysis is surprisingly predictive at moderate and high surface viscosities. Equal surface viscosities decrease the Taylor deformation parameter and tank-treading angle and also strongly modify the dynamics of the droplet: when the Boussinesq number (surface viscosity) is large relative to the capillary number (surface tension), the droplet displays damped oscillations prior to steady-state tank-treading, reminiscent from the behaviour at large viscosity contrast. In the limit of infinite capillary number
$B_{q}$. Then, influence of equal surface viscosities on steady-state characteristics of a droplet in shear flow are studied, considering both small and large deformations and for a large range of bulk viscosity contrast. We find that small deformation analysis is surprisingly predictive at moderate and high surface viscosities. Equal surface viscosities decrease the Taylor deformation parameter and tank-treading angle and also strongly modify the dynamics of the droplet: when the Boussinesq number (surface viscosity) is large relative to the capillary number (surface tension), the droplet displays damped oscillations prior to steady-state tank-treading, reminiscent from the behaviour at large viscosity contrast. In the limit of infinite capillary number 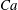 $Ca$, such oscillations are permanent. The influence of surface viscosities on breakup is also investigated, and results show that the critical capillary number is increased. A diagram
$Ca$, such oscillations are permanent. The influence of surface viscosities on breakup is also investigated, and results show that the critical capillary number is increased. A diagram 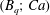 $(B_{q};Ca)$ of breakup is established with the same inner and outer bulk viscosities. Additionally, the separate roles of shear and dilational surface viscosity are also elucidated, extending results from small deformation analysis. Indeed, shear (dilational) surface viscosity increases (decreases) the stability of drops to breakup under shear flow. The steady-state deformation (Taylor parameter) varies nonlinearly with each Boussinesq number or a linear combination of both Boussinesq numbers. Finally, the study shows that for certain combinations of shear and dilational viscosities, drop deformation for a given capillary number is the same as in the case of a clean surface while the inclination angle varies.
$(B_{q};Ca)$ of breakup is established with the same inner and outer bulk viscosities. Additionally, the separate roles of shear and dilational surface viscosity are also elucidated, extending results from small deformation analysis. Indeed, shear (dilational) surface viscosity increases (decreases) the stability of drops to breakup under shear flow. The steady-state deformation (Taylor parameter) varies nonlinearly with each Boussinesq number or a linear combination of both Boussinesq numbers. Finally, the study shows that for certain combinations of shear and dilational viscosities, drop deformation for a given capillary number is the same as in the case of a clean surface while the inclination angle varies.
- Type
- Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © 2016 Cambridge University Press
References
- 72
- Cited by



