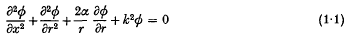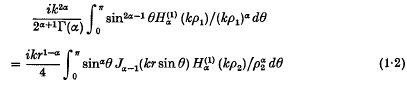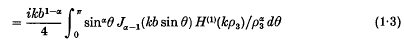Research Article
Martingale inequalities
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 October 2008, pp. 377-382
-
- Article
- Export citation
Modifications of Fourier transforms and singular continuous measures
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 October 2008, pp. 383-392
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Hughes problem for exponent nine
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 October 2008, pp. 393-399
-
- Article
- Export citation
The projective characters of the Mathieu group M12 and of its automorphism group
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 October 2008, pp. 401-412
-
- Article
- Export citation
Stable range in C*-algebras
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 October 2008, pp. 413-418
-
- Article
- Export citation
On homomorphisms between Weyl modules and Specht modules
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 October 2008, pp. 419-425
-
- Article
- Export citation
A stratification of the space of cubic surfaces
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 October 2008, pp. 427-441
-
- Article
- Export citation
Manifolds with multiple knot-surgery descriptions
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 October 2008, pp. 443-448
-
- Article
- Export citation
On conjectures of Mahowald, Segal and Sullivan
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 October 2008, pp. 449-458
-
- Article
- Export citation
Calculation of Lin's Ext groups
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 October 2008, pp. 459-469
-
- Article
- Export citation
Unilateral quasi-regularizers of closed operators
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 October 2008, pp. 471-480
-
- Article
- Export citation
A note on surface geometry with special reference to twist
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 October 2008, pp. 481-487
-
- Article
- Export citation
Galerkin approximations in several parameter bifurcation problems
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 October 2008, pp. 489-500
-
- Article
- Export citation
Strict convexity, strong ellipticity, and regularity in the calculus of variations
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 October 2008, pp. 501-513
-
- Article
- Export citation
The fundamental solution for the axially symmetric wave equation II
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 October 2008, pp. 515-521
-
- Article
- Export citation
On bundle completion of parallelizable manifolds
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 October 2008, pp. 523-525
-
- Article
- Export citation
Conditions for the local existence of metric in a generic affine manifold
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 October 2008, pp. 527-534
-
- Article
- Export citation
Corrigenda
The inhomogeneous minimum of binary quadratic, ternary cubic and quaternary quartic forms - Corrigenda
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 October 2008, p. 534
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Calculation of Lin's Ext groups - Corrigenda
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 October 2008, p. 534
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Front matter
PSP volume 87 issue 3 Cover and Front matter
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 October 2008, pp. f1-f2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation

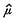 vanishes at infinity is continuous, and generally, that μ is continuous if and only if
vanishes at infinity is continuous, and generally, that μ is continuous if and only if 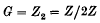
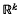 ,
,