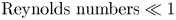60 results
Decreased risk of non-influenza respiratory infection after influenza B virus infection in children
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 April 2024, e60
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Radiofrequency ice dielectric measurements at Summit Station, Greenland
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 October 2023, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Imaging and Molecular Annotation of Xenographs and Tumours (IMAXT): High throughput data and analysis infrastructure
-
- Journal:
- Biological Imaging / Volume 3 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 April 2023, e11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Largest-known fossil penguin provides insight into the early evolution of sphenisciform body size and flipper anatomy
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Paleontology / Volume 97 / Issue 2 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 February 2023, pp. 434-453
-
- Article
- Export citation
Processing of social and monetary rewards in autism spectrum disorders
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 222 / Issue 3 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 January 2023, pp. 100-111
- Print publication:
- March 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Socio-economic factors correlating with illegal use of giraffe body parts
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Volumetric evolution of elastic turbulence in porous media
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 950 / 10 November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 October 2022, A36
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Nasogastric tube feeding under physical restraint on paediatric wards: ethical, legal and practical considerations regarding this lifesaving intervention
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Bulletin / Volume 47 / Issue 2 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 March 2022, pp. 105-110
- Print publication:
- April 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Microtomographic particle image velocimetry measurements of viscoelastic instabilities in a three-dimensional microcontraction
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 923 / 25 September 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 August 2021, R6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Rangeland loss and population decline of the critically endangered Liben Lark Heteromirafra archeri in southern Ethiopia
-
- Journal:
- Bird Conservation International / Volume 32 / Issue 1 / March 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2021, pp. 64-77
-
- Article
- Export citation
Mental health before and during the COVID-19 pandemic in two longitudinal UK population cohorts
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 218 / Issue 6 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 November 2020, pp. 334-343
- Print publication:
- June 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Antarctic ice sheet response to sudden and sustained ice-shelf collapse (ABUMIP)
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology / Volume 66 / Issue 260 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 September 2020, pp. 891-904
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Meeting nutritional targets of critically ill patients by combined enteral and parenteral nutrition: review and rationale for the EFFORTcombo trial
-
- Journal:
- Nutrition Research Reviews / Volume 33 / Issue 2 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2020, pp. 312-320
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Co-occurring trajectories of anxiety and insistence on sameness behaviour in autism spectrum disorder
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 218 / Issue 1 / January 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 July 2020, pp. 20-27
- Print publication:
- January 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
An ultra-wide bandwidth (704 to 4 032 MHz) receiver for the Parkes radio telescope
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 37 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 April 2020, e012
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
20 - Deep Carbon through Deep Time
-
-
- Book:
- Deep Carbon
- Published online:
- 03 October 2019
- Print publication:
- 17 October 2019, pp 620-652
-
- Chapter
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
5 - Diamonds and the Mantle Geodynamics of Carbon
-
-
- Book:
- Deep Carbon
- Published online:
- 03 October 2019
- Print publication:
- 17 October 2019, pp 89-128
-
- Chapter
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Expression of cholesterol packaging and transport genes in human and rat placenta: impact of obesity and a high-fat diet
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease / Volume 11 / Issue 3 / June 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 October 2019, pp. 222-227
-
- Article
- Export citation
Equivalency of the diagnostic accuracy of the PHQ-8 and PHQ-9: a systematic review and individual participant data meta-analysis – ERRATUM
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 50 / Issue 16 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 August 2019, p. 2816
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Titans of the early Universe: The Prato statement on the origin of the first supermassive black holes
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 36 / 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 August 2019, e027
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation