FESEM image of porous Li1.2Ni0.13Co0.13Mn0.54O2. [Y. Jiang, H. Zhuang, Q. Ma, Z. Jiao, H. Zhang, R. Liu, Y. Chu, and B. Zhao: Synthesis of porous Li2MnO3-LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 nanoplates via colloidal crystal template. p. 1505].
Articles
Nonequilibrium grain size distribution with generalized growth and nucleation rates
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 June 2013, pp. 1407-1412
-
- Article
- Export citation
Variation of crystal quality and residual stresses in epitaxially grown thin film systems induced by ion implantation and annealing
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 May 2013, pp. 1413-1419
-
- Article
- Export citation
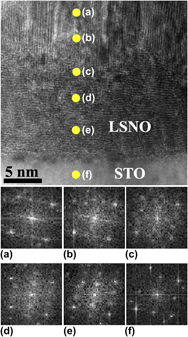
Heteroepitaxy and crystallographic orientation transition in La1.875Sr0.125NiO4 thin films on single crystal SrTiO3
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 May 2013, pp. 1420-1431
-
- Article
- Export citation
The microstructural and optical properties of Ge/Si heterostructures grown by low-temperature molecular beam epitaxy
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 May 2013, pp. 1432-1441
-
- Article
- Export citation
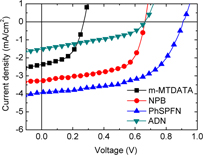
Improvement in the open-circuit voltage of an organic photovoltaic device through selection of a suitable and low-lying highest occupied molecular orbital for the electron donor layer
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 May 2013, pp. 1442-1448
-
- Article
- Export citation
Synthesis of positively charged polyelectrolyte multilayer membranes for removal of divalent metal ions
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 May 2013, pp. 1449-1457
-
- Article
- Export citation
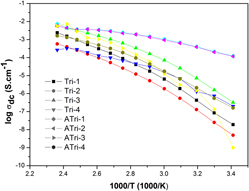
Sulfonated poly(vinyl alcohol)/triazole blends as anhydrous proton conducting membranes for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 May 2013, pp. 1458-1465
-
- Article
- Export citation
Size-dependent carrier dynamics and activation energy in CdTe/ZnTe quantum dots on Si substrates
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 May 2013, pp. 1466-1470
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effective optoelectronic and photocatalytic response of Eu3+-doped TiO2 nanoscale systems synthesized via a rapid condensation technique
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 May 2013, pp. 1471-1480
-
- Article
- Export citation
Optical and upconversion properties of Er3+-doped oxyfluoride transparent glass-ceramics containing SrF2 nanocrystals
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 May 2013, pp. 1481-1489
-
- Article
- Export citation
Facile synthesis of poly(methylsilsesquioxane) and MgO nanoparticle composite dielectrics
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 May 2013, pp. 1490-1497
-
- Article
- Export citation
Polyanion modulated evolution of perovskite BiFeO3 microspheres to microcubes by a microwave assisted hydrothermal method
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 May 2013, pp. 1498-1504
-
- Article
- Export citation
Synthesis of porous Li2MnO3-LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 nanoplates via colloidal crystal template
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 May 2013, pp. 1505-1511
-
- Article
- Export citation
Room-temperature gelcasting of alumina with a water-soluble copolymer
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 May 2013, pp. 1512-1516
-
- Article
- Export citation
Densification kinetics, phase assemblage and hardness of spark plasma sintered Cu–10 wt% TiB2 and Cu–10 wt% TiB2–10 wt% Pb composites
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 May 2013, pp. 1517-1528
-
- Article
- Export citation
Precipitation kinetics of M23C6 in T/P92 heat-resistant steel by applying soft-impingement correction
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 May 2013, pp. 1529-1537
-
- Article
- Export citation
Front Cover (OFC, IFC) and matter
JMR volume 28 issue 11 Cover and Front matter
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 June 2013, pp. f1-f5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Back Cover (OBC, IBC) and matter
JMR volume 28 issue 11 Cover and Back matter
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 June 2013, pp. b1-b3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation