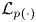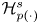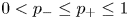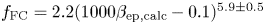27 results
ENVIRONMENT-BASED DESIGN (EBD): USING ONLY NECESSARY KNOWLEDGE FOR DESIGNER CREATIVITY
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Design Society / Volume 3 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 June 2023, pp. 1675-1684
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Association between time-restricted eating and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in a nationwide cross-sectional study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 130 / Issue 10 / 28 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2023, pp. 1787-1794
- Print publication:
- 28 November 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Machine learning in requirements elicitation: a literature review
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Healthy and unhealthy low-carbohydrate diets and plasma markers of cardiometabolic risk
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 130 / Issue 1 / 14 July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2022, pp. 137-146
- Print publication:
- 14 July 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
The global disease burden attributable to a diet low in fibre in 204 countries and territories from 1990 to 2019
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 26 / Issue 4 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 September 2022, pp. 854-865
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Geochronology, geochemistry and tectonic implications of early Carboniferous plutons in the southwestern Alxa Block
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 159 / Issue 3 / March 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 November 2021, pp. 372-388
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Smart designing of smart systems
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
New variable martingale Hardy spaces
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 152 / Issue 2 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 April 2021, pp. 450-478
- Print publication:
- April 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dependence of fishbone cycle on energetic particle intensity in EAST low-magnetic-shear plasmas
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 86 / Issue 6 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 December 2020, 905860610
-
- Article
- Export citation
A tEEG framework for studying designer’s cognitive and affective states
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Design Science / Volume 6 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 November 2020, e29
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Diet and liver cancer risk: a narrative review of epidemiological evidence
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 124 / Issue 3 / 14 August 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 April 2020, pp. 330-340
- Print publication:
- 14 August 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Glacial events during the last glacial termination in the Pagele valley, Qiongmu Gangri peak, southern Tibetan Plateau, and their links to oceanic and atmospheric circulation
-
- Journal:
- Quaternary Research / Volume 95 / May 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 March 2020, pp. 129-141
-
- Article
- Export citation
Influence of Information Collection Strategy on Designer’s Mental Stress
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Design Society: International Conference on Engineering Design / Volume 1 / Issue 1 / July 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 July 2019, pp. 1783-1792
- Print publication:
- July 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Miniaturized tri-band filtering-response power divider with short- and open-stub-loaded resonators
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies / Volume 9 / Issue 8 / October 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 August 2017, pp. 1637-1643
-
- Article
- Export citation
Laboratory astrophysics with laser-driven strong magnetic fields in China
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 4 / 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 August 2016, e27
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Nε-(carboxymethyl)-lysine, White Matter, and Cognitive Function in Diabetes Patients
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 43 / Issue 4 / July 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 February 2016, pp. 518-522
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation