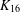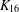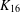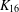194 results
The Alluvial Geoarchaeology of the Upper River Kennet in the Avebury Landscape: a Monumental Transformation of a Stable Landscape
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Prehistoric Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 May 2024, pp. 1-35
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Reflectance Transformation Imaging for the Recording of Incised Graffiti: A Case Study from the Maya Site of Holtun, Guatemala
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Archaeological Practice , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2024, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Hepatitis B in Africa Collaborative Network: cohort profile and analysis of baseline data
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 April 2023, e65
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The dynamic efficiency of gifting
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Institutional Economics / Volume 19 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 August 2022, pp. 70-85
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Effect of Self-Paced Exercise Intensity and Cardiorespiratory Fitness on Frontal Grey Matter Volume in Cognitively Normal Older Adults: A Randomised Controlled Trial
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 28 / Issue 9 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 September 2021, pp. 902-915
-
- Article
- Export citation
Characterisation of age and polarity at onset in bipolar disorder
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 219 / Issue 6 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 August 2021, pp. 659-669
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
1 - Variability of the Oceans
-
-
- Book:
- Interacting Climates of Ocean Basins
- Published online:
- 13 January 2021
- Print publication:
- 26 November 2020, pp 1-53
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
SHAFTESBURY ON SELFISHNESS AND PARTISANSHIP
-
- Journal:
- Social Philosophy and Policy / Volume 37 / Issue 1 / Summer 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2021, pp. 55-79
- Print publication:
- Summer 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Validity of predictive equations to estimate RMR in females with varying BMI - CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Nutritional Science / Volume 9 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 June 2020, e22
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Validity of predictive equations to estimate RMR in females with varying BMI
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Nutritional Science / Volume 9 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 May 2020, e17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Identifying schizophrenia patients who carry pathogenic genetic copy number variants using standard clinical assessment: retrospective cohort study
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 216 / Issue 5 / May 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 January 2020, pp. 275-279
- Print publication:
- May 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
A Philosopher in his Closet: Reflexivity and Justification in Hume's Moral Theory
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Philosophy / Volume 26 / Issue 2 / June 1996
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2020, pp. 231-255
-
- Article
- Export citation
Uneven use of biodiversity indicators in 5th National Reports to the Convention on Biological Diversity
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Environmental Conservation / Volume 47 / Issue 1 / March 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 December 2019, pp. 15-21
-
- Article
- Export citation
Detecting schizophrenia at the level of the individual: relative diagnostic value of whole-brain images, connectome-wide functional connectivity and graph-based metrics
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 50 / Issue 11 / August 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 August 2019, pp. 1852-1861
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
PERFECT 1-FACTORISATIONS OF
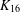 $K_{16}$
$K_{16}$
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 101 / Issue 2 / April 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 August 2019, pp. 177-185
- Print publication:
- April 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Chapter 8 - Communicating as business professionals
- from Part Two - Communicating in organisations
-
- Book:
- Communication Skills for Business Professionals
- Published online:
- 06 April 2020
- Print publication:
- 12 June 2019, pp 212-237
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
How To Use This Textbook and Its Vitalsource Interactive Elements
-
- Book:
- Communication Skills for Business Professionals
- Published online:
- 06 April 2020
- Print publication:
- 12 June 2019, pp xv-xvii
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Preface
-
- Book:
- Communication Skills for Business Professionals
- Published online:
- 06 April 2020
- Print publication:
- 12 June 2019, pp xi-xi
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Chapter 5 - Persuasion, conflict management and negotiation
- from Part One - Understanding communication
-
- Book:
- Communication Skills for Business Professionals
- Published online:
- 06 April 2020
- Print publication:
- 12 June 2019, pp 104-140
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Glossary
-
- Book:
- Communication Skills for Business Professionals
- Published online:
- 06 April 2020
- Print publication:
- 12 June 2019, pp 450-459
-
- Chapter
- Export citation