49 results
Analysis of microbiological tests in patients withholding or withdrawing life-sustaining treatment at the end stage of life in 2 Korean hospitals
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 45 / Issue 2 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. 201-206
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
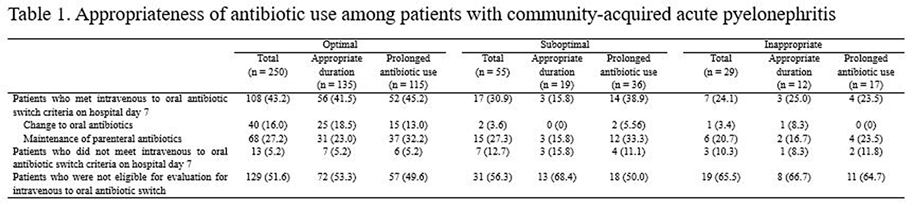
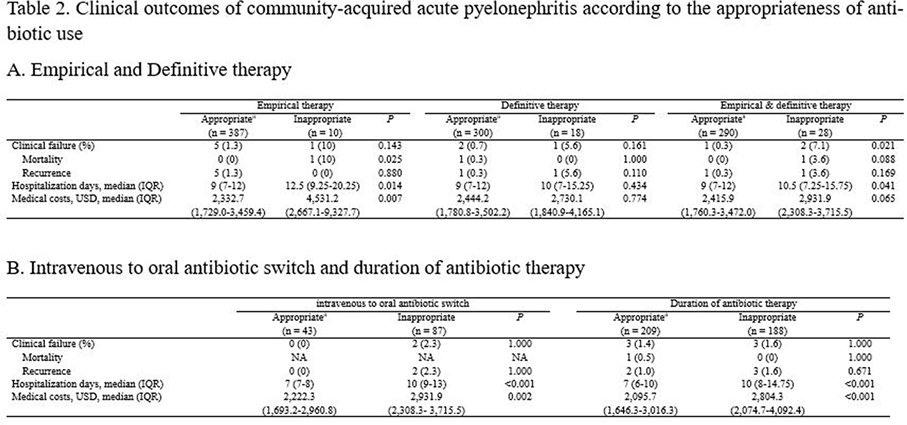
Differences in the Clinical Outcome of Community-Acquired APN According to the Appropriateness of Antibiotic Use
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 1 / Issue S1 / July 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 July 2021, p. s6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Clinical impact of early reinsertion of a central venous catheter after catheter removal in patients with catheter-related bloodstream infections
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 42 / Issue 2 / February 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 September 2020, pp. 162-168
- Print publication:
- February 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Association of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and serum total cholesterol with depressive symptoms in Korean adults: the Fifth Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES V, 2010–2012)
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 20 / Issue 10 / July 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 July 2016, pp. 1836-1843
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
A Novel Exon 3 Mutation (P66S) in the SOD1 Gene in Familial ALS
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 39 / Issue 2 / March 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 December 2014, pp. 245-246
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A change in social activity and depression among Koreans aged 45 years and more: analysis of the Korean Longitudinal Study of Aging (2006–2010)
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 27 / Issue 4 / April 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2014, pp. 629-637
-
- Article
- Export citation
A normative study of total scores of the CERAD neuropsychological assessment battery in an educationally diverse elderly population
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 26 / Issue 11 / November 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 July 2014, pp. 1897-1904
-
- Article
- Export citation
Borna disease virus and deficit schizophrenia
-
- Journal:
- Acta Neuropsychiatrica / Volume 15 / Issue 5 / October 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 June 2014, pp. 262-265
-
- Article
- Export citation
Electron Holography Study of the Charging Effect in Microfibrils of Sciatic Nerve Tissues
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 19 / Issue S5 / August 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 August 2013, pp. 54-57
- Print publication:
- August 2013
-
- Article
- Export citation
Three-Dimensional Imaging of Cerebellar Mossy Fiber Rosettes by Ion-Abrasion Scanning Electron Microscopy
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 19 / Issue S5 / August 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 August 2013, pp. 172-177
- Print publication:
- August 2013
-
- Article
- Export citation
Adaptive Phenotypic Plasticity of Siberian Elm in Response to Drought Stress: Increased Stomatal Pore Depth
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 19 / Issue S5 / August 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 August 2013, pp. 178-181
- Print publication:
- August 2013
-
- Article
- Export citation
New perspectives on habitat selection by the Black-faced Spoonbill Platalea minor based upon satellite telemetry
-
- Journal:
- Bird Conservation International / Volume 23 / Issue 4 / December 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 March 2013, pp. 495-501
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Role of severity and gender in the association between late-life depression and all-cause mortality
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 25 / Issue 4 / April 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2012, pp. 677-684
-
- Article
- Export citation
Magnesium and calcium deficiencies additively increase zinc concentrations and metallothionein expression in the rat liver
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 109 / Issue 3 / 14 February 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 May 2012, pp. 425-432
- Print publication:
- 14 February 2013
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Morphology of Foliar Trichomes of the Chinese Cork Oak Quercus variabilis by Electron Microscopy and Three-Dimensional Surface Profiling
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 17 / Issue 3 / June 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 May 2011, pp. 461-468
- Print publication:
- June 2011
-
- Article
- Export citation
Opto-electrical characterization and X-ray Mapping of large-volume cadmium zinc telluride radiation detectors
-
- Journal:
- MRS Online Proceedings Library Archive / Volume 1164 / 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2011, 1164-L10-07
- Print publication:
- 2009
-
- Article
- Export citation
Adsorption and Reaction Behaviors of Hf Precursor with Two Hydroxyls on Si(100): First Principles Study
-
- Journal:
- MRS Online Proceedings Library Archive / Volume 1155 / 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2011, 1155-C09-14
- Print publication:
- 2009
-
- Article
- Export citation
The beneficial effect of the sap of Acer mono in an animal with low-calcium diet-induced osteoporosis-like symptoms
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 100 / Issue 5 / November 2008
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 November 2008, pp. 1011-1018
- Print publication:
- November 2008
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Characterizations of Real Hypersurfaces in a Complex Space Form
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 50 / Issue 1 / 01 March 2007
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2018, pp. 97-104
- Print publication:
- 01 March 2007
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation