Article contents
Hardy–Littlewood–Sobolev inequality and existence of the extremal functions with extended kernel
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 31 October 2022
Abstract
In this paper, we consider the following Hardy–Littlewood–Sobolev inequality with extended kernel(0.1)
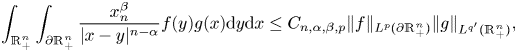
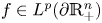 , $g\in L^{q'}(\mathbb {R}_+^{n})$
, $g\in L^{q'}(\mathbb {R}_+^{n})$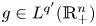 and $p,\,\ q'\in (1,\,\infty )$
and $p,\,\ q'\in (1,\,\infty )$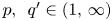 , $\beta \geq 0$
, $\beta \geq 0$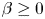 , $\alpha +\beta >1$
, $\alpha +\beta >1$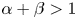 such that $\frac {n-1}{n}\frac {1}{p}+\frac {1}{q'}-\frac {\alpha +\beta -1}{n}=1$
such that $\frac {n-1}{n}\frac {1}{p}+\frac {1}{q'}-\frac {\alpha +\beta -1}{n}=1$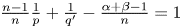 .
.We prove the existence of all extremal functions for (0.1). We show that if $f$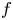 and $g$
and $g$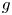 are extremal functions for (0.1) then both of $f$
are extremal functions for (0.1) then both of $f$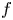 and $g$
and $g$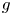 are radially decreasing. Moreover, we apply the regularity lifting method to obtain the smoothness of extremal functions. Finally, we derive the sufficient and necessary condition of the existence of any nonnegative nontrivial solutions for the Euler–Lagrange equations by using Pohozaev identity.
are radially decreasing. Moreover, we apply the regularity lifting method to obtain the smoothness of extremal functions. Finally, we derive the sufficient and necessary condition of the existence of any nonnegative nontrivial solutions for the Euler–Lagrange equations by using Pohozaev identity.
Keywords
MSC classification
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh Section A: Mathematics , Volume 153 , Issue 5 , October 2023 , pp. 1683 - 1705
- Copyright
- Copyright © The Author(s), 2022. Published by Cambridge University Press on behalf of The Royal Society of Edinburgh
References
- 4
- Cited by



