Article contents
The Absolute Summability (A) of Fourier Series
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 January 2009
Extract
In a recent paper Dr J. M. Whittaker has shown that the Fourier series
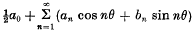
of a function f(θ) which has a Lebesgue integral in (— π, π), is absolutely summable (A) to sum l, if

exists, where
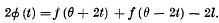 .
.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society , Volume 2 , Issue 3 , January 1931 , pp. 129 - 134
- Copyright
- Copyright © Edinburgh Mathematical Society 1931
References
page 129 note 1 Proc. Edinburgh Math. Soc. (2), 2 (1930), 1–5.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
page 129 note 2 A series
has been defined to be absolutely summable (A), if
is convergent in ( 0 ≤ x < 1) and if f(x) is of bounded variation in (0, 1).
page 130 note 1 Hobson, E. W., Theory of Functions of a Real Variable, 2 (1926), 629.Google Scholar
page 130 note 2 ibid.. 1 (1927), 630.
page 131 note 1 ibid.. 593.
page 133 note 1 See Hardy, G. H., Messenger of Math., 49 (1919–1920), 150.Google Scholar
page 134 note 1 Abhand. d. Bayer. Akad. (1876), II, 37.Google ScholarSee also Hardy, G. H., Quarterly Journal, 44 (1913), 242–263.Google Scholar
- 3
- Cited by


