Article contents
Electrical and Structural Characterization of Ti Contacts to Si0.89 Ge0.11/Si(001) Epilayers
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 15 February 2011
Abstract
The properties of thin (350 Å) Ti layers deposited on Si0.89Ge0.11 layers epitaxially grown on Si(001) were studied as a function of isochronal (30 min.) thermal treatments in the temperature range Ta=550–800°C. Both as-deposited and annealed at Ta up to 750°C Schottky diodes revealed near-ideal I–V and C–V characteristics with the same flat-band barrier height 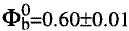 eV. The results indicate that at these Ta the Fermi level is pinned with respect to the conduction band.
eV. The results indicate that at these Ta the Fermi level is pinned with respect to the conduction band.
Annealing at 800°C resulted in an improvement of the Schottky diodes quality and a drop in  and the series resistance Rs of the contacts. The values of the ideality factor n and (
and the series resistance Rs of the contacts. The values of the ideality factor n and ( measured were 1.03±0.02 and 0.56±0.007 eV, correspondingly. The electrical parameters of these metal/semiconductor contacts were correlated with the dynamics of interfacial reactions due to the applied heat-treatments.
measured were 1.03±0.02 and 0.56±0.007 eV, correspondingly. The electrical parameters of these metal/semiconductor contacts were correlated with the dynamics of interfacial reactions due to the applied heat-treatments.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 1996
References
- 4
- Cited by


