Article contents
Multilayer multifunctional advanced coatings for receivers of concentrated solar power plants
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 19 September 2019
Abstract
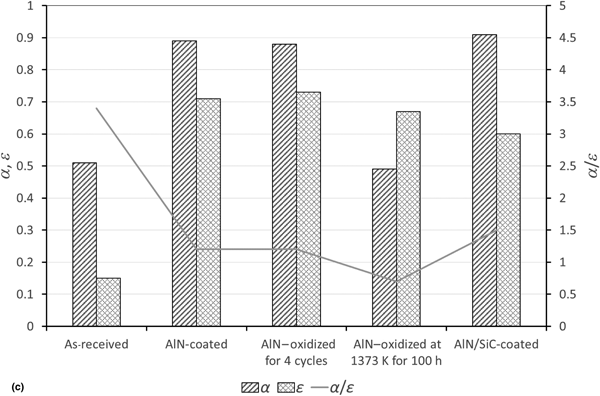
The extending market of concentrated solar power plants requires high-temperature materials for solar surface receivers that would ideally heat an air coolant beyond 1300 K. This work presents investigation on high-temperature alloys with ceramic coatings (AlN or SiC/AlN stacking) to combine the properties of the substrate (creep resistance, machinability) and coating (slow oxidation kinetics, high solar absorptivity). The first results showed that high-temperature oxidation resistance and optical properties of metallic alloys were improved by the different coatings. However, the fast thermal shocks led to high stress levels not compatible due to the differences in thermal expansion coefficients.
- Type
- Research Letters
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2019
References
- 1
- Cited by



