Article contents
Coherent structures and dominant frequencies in a turbulent three-dimensional diffuser
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 12 April 2012
Abstract
Dominant frequencies and coherent structures are investigated in a turbulent, three-dimensional and separated diffuser flow at  (based on bulk velocity and inflow-duct height), where mean flow characteristics were first studied experimentally by Cherry, Elkins and Eaton (Intl J. Heat Fluid Flow, vol. 29, 2008, pp. 803–811) and later numerically by Ohlsson et al. (J. Fluid Mech., vol. 650, 2010, pp. 307–318). Coherent structures are educed by proper orthogonal decomposition (POD) of the flow, which together with time probes located in the flow domain are used to extract frequency information. The present study shows that the flow contains multiple phenomena, well separated in frequency space. Dominant large-scale frequencies in a narrow band
(based on bulk velocity and inflow-duct height), where mean flow characteristics were first studied experimentally by Cherry, Elkins and Eaton (Intl J. Heat Fluid Flow, vol. 29, 2008, pp. 803–811) and later numerically by Ohlsson et al. (J. Fluid Mech., vol. 650, 2010, pp. 307–318). Coherent structures are educed by proper orthogonal decomposition (POD) of the flow, which together with time probes located in the flow domain are used to extract frequency information. The present study shows that the flow contains multiple phenomena, well separated in frequency space. Dominant large-scale frequencies in a narrow band 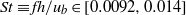 (where
(where 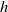 is the inflow-duct height and
is the inflow-duct height and 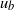 is the bulk velocity), yielding time periods
is the bulk velocity), yielding time periods 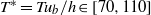 , are deduced from the time signal probes in the upper separated part of the diffuser. The associated structures identified by the POD are large streaks arising from a sinusoidal oscillating motion in the diffuser. Their individual contributions to the total kinetic energy, dominated by the mean flow, are, however, small. The reason for the oscillating movement in this low-frequency range is concluded to be the confinement of the flow in this particular geometric set-up in combination with the high Reynolds number and the large separated zone on the top diffuser wall. Based on this analysis, it is shown that the bulk of the streamwise root mean square (r.m.s.) value arises due to large-scale motion, which in turn can explain the appearance of two or more peaks in the streamwise r.m.s. value. The weak secondary flow present in the inflow duct is shown to survive into the diffuser, where it experiences an imbalance with respect to the upper expanding corners, thereby giving rise to the asymmetry of the mean separated region in the diffuser.
, are deduced from the time signal probes in the upper separated part of the diffuser. The associated structures identified by the POD are large streaks arising from a sinusoidal oscillating motion in the diffuser. Their individual contributions to the total kinetic energy, dominated by the mean flow, are, however, small. The reason for the oscillating movement in this low-frequency range is concluded to be the confinement of the flow in this particular geometric set-up in combination with the high Reynolds number and the large separated zone on the top diffuser wall. Based on this analysis, it is shown that the bulk of the streamwise root mean square (r.m.s.) value arises due to large-scale motion, which in turn can explain the appearance of two or more peaks in the streamwise r.m.s. value. The weak secondary flow present in the inflow duct is shown to survive into the diffuser, where it experiences an imbalance with respect to the upper expanding corners, thereby giving rise to the asymmetry of the mean separated region in the diffuser.
JFM classification
- Type
- Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Cambridge University Press 2012
References
- 25
- Cited by


