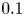51 results
Sustained Antibacterial Effect of Levofloxacin Drug in a Polymer Matrix by Hybridization With A Layered Double Hydroxide
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 69 / Issue 4 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 443-452
-
- Article
- Export citation
TPX2 Serves as a Cancer Susceptibility Gene and Is Closely Associated with the Poor Prognosis of Endometrial Cancer
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e70
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Geochemistry, zircon U–Pb geochronology and Hf isotope of the early Permian gabbro and high-Mg diorites from the Zhusileng–Hangwula Belt in the northern Alxa area: Petrogenesis and tectonic implications
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 160 / Issue 7 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 August 2023, pp. 1417-1427
-
- Article
- Export citation
Prehospital Nursing Volunteer’s Personality Traits: A Motivational Perspective
-
- Journal:
- Prehospital and Disaster Medicine / Volume 38 / Issue S1 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 July 2023, p. s162
- Print publication:
- May 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Another emerging threat to birds: avian mortality estimates from roadside transparent noise barrier collisions in South Korea
-
- Journal:
- Bird Conservation International / Volume 33 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 March 2023, e50
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The occurrence and prevention of mental diseases after osteoarthritis in the lateral compartment of the knee
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 March 2023, p. S36
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Field observations of surface ruptures accompanying a tsunami and supershear earthquake along a plate boundary strike-slip fault
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 159 / Issue 6 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 February 2022, pp. 893-903
-
- Article
- Export citation
Multiple Cognitive and Behavioral Factors Link Association Between Brain Structure and Functional Impairment of Daily Instrumental Activities in Older Adults
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 28 / Issue 7 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 July 2021, pp. 673-686
-
- Article
- Export citation
Rarefied flow separation in microchannel with bends
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 901 / 25 October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 August 2020, A26
-
- Article
- Export citation
Disaster Response to a Mass Casualty Incident in a Hospital Fire by Regional Disaster Medical Assistance Team: Characteristics of Hospital Fire
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 16 / Issue 1 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 August 2020, pp. 8-11
-
- Article
- Export citation
Study protocol on Enhanced Primary Healthcare (EnPHC) interventions: a quasi-experimental controlled study on diabetes and hypertension management in primary healthcare clinics
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Primary Health Care Research & Development / Volume 21 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 August 2020, e27
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Associations of fat and carbohydrate intake with becoming overweight and obese: an 11-year longitudinal cohort study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 124 / Issue 7 / 14 October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 May 2020, pp. 715-728
- Print publication:
- 14 October 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Deep-learning-based phase control method for tiled aperture coherent beam combining systems
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 7 / 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 November 2019, e59
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Underground nuclear astrophysics experiment JUNA in China
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 15 / Issue S350 / April 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 October 2020, pp. 313-320
- Print publication:
- April 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Formation of low-angle grain boundaries under different solidification conditions in the rejoined platforms of Ni-based single crystal superalloys
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 2 / 28 January 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 November 2018, pp. 251-260
- Print publication:
- 28 January 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Far-Field High-Energy Diffraction Microscopy: A Non-Destructive Tool for Characterizing the Microstructure and Micromechanical State of Polycrystalline Materials
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy Today / Volume 25 / Issue 5 / September 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 August 2017, pp. 36-45
- Print publication:
- September 2017
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Anti-torque systems of electromechanical cable-suspended drills and test results
-
- Journal:
- Annals of Glaciology / Volume 55 / Issue 68 / 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 July 2017, pp. 207-218
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Identification of Reference Genes for Studying Herbicide Resistance Mechanisms in Japanese Foxtail (Alopecurus japonicus)
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 65 / Issue 5 / September 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 June 2017, pp. 557-566
-
- Article
- Export citation
Climate change and social vicissitudes in China over the past two millennia
-
- Journal:
- Quaternary Research / Volume 86 / Issue 2 / September 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 January 2017, pp. 133-143
-
- Article
- Export citation