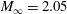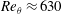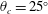76 results
Synthesis, Structure, and Ferroelectricity of a Kaolinite-p--Aminobenzamide Intercalation Compound
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 67 / Issue 6 / December 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 461-470
-
- Article
- Export citation
Today, tomorrow, and then forever: Exploring how workflow experience is sustained from a work–home perspective
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Management & Organization , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 November 2023, pp. 1-22
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Evaluation of the Plasticity of Novel Regulatory Cells—Telocytes—in the Gonad of the Male Chinese Soft-Shelled Turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis) Associated with Seasonal Reproductive Activity
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 October 2022, pp. 2069-2077
- Print publication:
- December 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
In-situ TEM imaging of Novel Edge Reconstruction in Bilayer Phosphorene
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2022, pp. 2310-2311
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A review of factors influencing the quality and sensory evaluation techniques applied to Greek yogurt
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Dairy Research / Volume 89 / Issue 2 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 April 2022, pp. 213-219
- Print publication:
- May 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Lochkovian (Lower Devonian) conodonts from the Alengchu section, western Yunnan, China
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Paleontology / Volume 96 / Issue 3 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 December 2021, pp. 638-657
-
- Article
- Export citation
Structural and functional analysis of p47 cofactor binding on the p97 disease mutant
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 27 / Issue S1 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 July 2021, pp. 1908-1910
- Print publication:
- August 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Modulation of turbulence by saltating particles on erodible bed surface
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 918 / 10 July 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 May 2021, A16
-
- Article
- Export citation
Exogenous salicylic acid improves resistance of aphid-susceptible wheat to the grain aphid, Sitobion avenae (F.) (Hemiptera: Aphididae)
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 111 / Issue 5 / October 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 April 2021, pp. 544-552
-
- Article
- Export citation
The impacts of COVID-19 outbreak on mental health in general population in different areas in China
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 52 / Issue 13 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 December 2020, pp. 2651-2660
-
- Article
- Export citation
Nano chitosan–zinc complex improves the growth performance and antioxidant capacity of the small intestine in weaned piglets
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 126 / Issue 6 / 28 September 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 December 2020, pp. 801-812
- Print publication:
- 28 September 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Effect of Ambient Temperature on Infectious Diarrhea and Diarrhea-like Illness in Wuxi, China
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 16 / Issue 2 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2020, pp. 583-589
-
- Article
- Export citation
FNDC5 polymorphism influences the association between sarcopenia and liver fibrosis in adults with biopsy-proven non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 126 / Issue 6 / 28 September 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 November 2020, pp. 813-824
- Print publication:
- 28 September 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Higher flavonoid intake is associated with a lower progression risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in adults: a prospective study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 125 / Issue 4 / 28 February 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 July 2020, pp. 460-470
- Print publication:
- 28 February 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Evaluating the effect of birth weight on brain volumes and depression: An observational and genetic study using UK Biobank cohort
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 63 / Issue 1 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 July 2020, e73
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Analysis of factors affecting the prognosis of COVID-19 patients and viral shedding duration
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 148 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 June 2020, e125
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A comparative investigation of long-term oxidation behavior of selective laser melting–fabricated Inconel 718 at 650 °C
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 15 / 14 August 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 May 2020, pp. 2036-2045
- Print publication:
- 14 August 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
An atlas of genetic correlations between psychiatric disorders and human blood plasma proteome
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 63 / Issue 1 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 February 2020, e17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Excessive gestational weight gain in the first trimester is associated with risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: a prospective study from Southwest China
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 23 / Issue 3 / February 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 December 2019, pp. 394-401
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Direct numerical simulation of conical shock wave–turbulent boundary layer interaction
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 877 / 25 October 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 August 2019, pp. 167-195
-
- Article
- Export citation