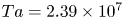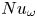38 results
Direct numerical simulation of Taylor–Couette flow with vertical asymmetric rough walls
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 975 / 25 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 November 2023, A30
-
- Article
- Export citation
INTERACTIVE EFFECTS PANEL DATA MODELS WITH GENERAL FACTORS AND REGRESSORS
-
- Journal:
- Econometric Theory , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 September 2023, pp. 1-17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
A compact 12 × 12 MIMO loop antenna for 5G mobile phone applications
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 June 2023, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
- Export citation
Efficacy of dynamic interpersonal therapy for major depressive disorder in China: results of a multicentered, three-arm, randomized, controlled trial
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 15 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 April 2023, pp. 7242-7254
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Protocol for a pharmacogenomic study on individualised antipsychotic drug treatment for patients with schizophrenia
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 7 / Issue 4 / July 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 June 2021, e121
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Iodine nutrition status of women after 10 years of Lipiodol supplementation: a cross-sectional study in Xinjiang, China
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 126 / Issue 1 / 14 July 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 October 2020, pp. 9-21
- Print publication:
- 14 July 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Metabolic syndrome and its relation to dietary patterns among a selected urbanised and semi-urbanised Tibetan population in transition from nomadic to settled living environment
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 24 / Issue 5 / April 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 April 2020, pp. 984-992
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Absence of contamination of personal protective equipment (PPE) by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 41 / Issue 5 / May 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 March 2020, pp. 614-616
- Print publication:
- May 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dietary administration of resistant starch improved caecal barrier function by enhancing intestinal morphology and modulating microbiota composition in meat duck
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 123 / Issue 2 / 28 January 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2019, pp. 172-181
- Print publication:
- 28 January 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
High-repetition-rate, high-peak-power 1450 nm laser source based on optical parametric chirped pulse amplification
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 7 / 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 May 2019, e32
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Underground nuclear astrophysics experiment JUNA in China
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 15 / Issue S350 / April 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 October 2020, pp. 313-320
- Print publication:
- April 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The evolutionary correlation associated with seed mass and altitude on nutrient allocation of seeds
-
- Journal:
- Seed Science Research / Volume 29 / Issue 1 / March 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2019, pp. 38-43
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effect of spheroidization of eutectic Si on mechanical properties of eutectic Al–Si alloys
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 33 / Issue 12 / 28 June 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2018, pp. 1773-1781
- Print publication:
- 28 June 2018
-
- Article
- Export citation
An Outbreak of Streptococcus pyogenes in a Mental Health Facility: Advantage of Well-Timed Whole-Genome Sequencing Over emm Typing
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 39 / Issue 7 / July 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 May 2018, pp. 852-860
- Print publication:
- July 2018
-
- Article
- Export citation
Assessment of thyroid function in children, adults and pregnant and lactating women after long-term salt iodisation measurements
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 119 / Issue 11 / 14 June 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2018, pp. 1245-1253
- Print publication:
- 14 June 2018
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Molecular clouds in the Extreme Outer Galaxy
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 13 / Issue S336 / September 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2018, pp. 187-188
- Print publication:
- September 2017
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Prevalence and risk factors for attempted suicide in the elderly: a cross-sectional study in Shanghai, China
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 29 / Issue 5 / May 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2016, pp. 709-715
-
- Article
- Export citation
Should urinary iodine concentrations of school-aged children continue to be used as proxy for different populations? Analysis of data from Chinese national surveys
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 116 / Issue 6 / 28 September 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 August 2016, pp. 1068-1076
- Print publication:
- 28 September 2016
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Laser performance of the SG-III laser facility
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 4 / 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 July 2016, e21
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Increased Fetal Plasma Erythropoietin in Monochorionic Twin Pregnancies With Selective Intrauterine Growth Restriction and Abnormal Umbilical Artery Doppler
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 19 / Issue 4 / August 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 May 2016, pp. 383-388
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation