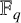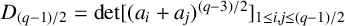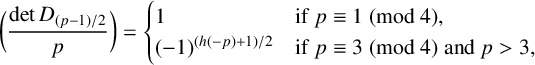74 results
ON GENERALISED LEGENDRE MATRICES INVOLVING ROOTS OF UNITY OVER FINITE FIELDS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 April 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Long-term warming altered soil physical structure and soil organic carbon pools in wheatland field
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Agriculture / Volume 60 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 January 2024, e1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Clay mineralogy across the P-T boundary of the Xiakou section, China: Evidence of clay provenance and environment
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 56 / Issue 2 / April 2008
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 131-143
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Experimental investigation of the stimulated Raman scattering effect in high-power nanosecond superfluorescent fiber source
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 September 2023, e88
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dissociation between neuroanatomical and symptomatic subtypes in schizophrenia
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 September 2023, e78
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Sustainability of the plastron on nano-grass-covered micro-trench superhydrophobic surfaces in high-speed flows of open water
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 962 / 10 May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 April 2023, A9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
1.2 kW all-fiber narrow-linewidth picosecond MOPA system
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 March 2023, e22
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effectiveness and optimal duration of early intervention treatment in adult-onset psychosis: a randomized clinical trial
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 6 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 February 2022, pp. 2339-2351
-
- Article
- Export citation
Influencing mechanisms of lifestyle and dietary factors on chronic diseases among community residents: updated evidence in Shanghai, China
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 25 / Issue 5 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 October 2021, pp. 1233-1245
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Midazolam for conscious sedation in transcatheter device closure of atrial septal defects guided solely by transthoracic echocardiography
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 32 / Issue 2 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 May 2021, pp. 282-286
-
- Article
- Export citation
Superhydrophobic drag reduction in high-speed towing tank
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 908 / 10 February 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 December 2020, A6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Inulin alleviates adverse metabolic syndrome and regulates intestinal microbiota composition in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fed with high-carbohydrate diet
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 126 / Issue 2 / 28 July 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 October 2020, pp. 161-171
- Print publication:
- 28 July 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Diet and liver cancer risk: a narrative review of epidemiological evidence
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 124 / Issue 3 / 14 August 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 April 2020, pp. 330-340
- Print publication:
- 14 August 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
High-rate lithium ion energy storage to facilitate increased penetration of photovoltaic systems in electricity grids - ADDENDUM
-
- Journal:
- MRS Energy & Sustainability / Volume 7 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 April 2020, E6
- Print publication:
- 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The CODATwins Project: The Current Status and Recent Findings of COllaborative Project of Development of Anthropometrical Measures in Twins
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 22 / Issue 6 / December 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 July 2019, pp. 800-808
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Underground nuclear astrophysics experiment JUNA in China
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 15 / Issue S350 / April 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 October 2020, pp. 313-320
- Print publication:
- April 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
High-rate lithium ion energy storage to facilitate increased penetration of photovoltaic systems in electricity grids
-
- Journal:
- MRS Energy & Sustainability / Volume 6 / 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 April 2019, E2
- Print publication:
- 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
STATISTICAL INFERENCE FOR MEASUREMENT EQUATION SELECTION IN THE LOG-REALGARCH MODEL
-
- Journal:
- Econometric Theory / Volume 35 / Issue 5 / October 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 November 2018, pp. 943-977
-
- Article
- Export citation