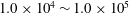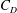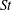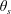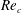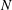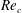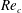84 results
Effect of Clay Charge on Swelling: A Clay-Modified Electrode Study
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 43 / Issue 5 / October 1995
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 607-614
-
- Article
- Export citation
Modified transseptal approach in endoscopic transsphenoidal pituitary surgery
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 137 / Issue 12 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2023, pp. 1409-1412
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Acceleration of 60 MeV proton beams in the commissioning experiment of the SULF-10 PW laser
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 10 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 August 2022, e26
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
P.160 Impact of peritumoral edema during tumor treatment field therapy: a computational modelling study
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 48 / Issue s3 / November 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2022, pp. S65-S66
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Institutional improvements in readability of written informed consent forms sustained post-revised Common Rule
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 5 / Issue 1 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2021, e192
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
FLEXIBLE SOIL MICROBIAL CARBON METABOLISM ACROSS AN ASIAN ELEVATION GRADIENT
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon / Volume 63 / Issue 5 / October 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2021, pp. 1397-1413
- Print publication:
- October 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Multispecies sustainability
-
- Journal:
- Global Sustainability / Volume 3 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 December 2020, e34
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Immediate and delayed psychological effects of province-wide lockdown and personal quarantine during the COVID-19 outbreak in China
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 52 / Issue 7 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 August 2020, pp. 1321-1332
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Characterization of flowing liquid films as a regenerating plasma mirror for high repetition-rate laser contrast enhancement
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 38 / Issue 2 / June 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 May 2020, pp. 128-134
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The southern Jiangsu coast is a critical moulting site for Spoon-billed Sandpiper Calidris pygmaea and Nordmann’s Greenshank Tringa guttifer
-
- Journal:
- Bird Conservation International / Volume 30 / Issue 4 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 May 2020, pp. 649-660
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Establishing a digital health platform in an academic medical center supporting rural communities
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 4 / Issue 5 / October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 April 2020, pp. 384-388
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
DIVERSITY AND DIVERSIFICATION RESEARCH
-
- Journal:
- Du Bois Review: Social Science Research on Race / Volume 15 / Issue 2 / Fall 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2019, pp. 245-255
-
- Article
- Export citation
Temporal changes in arthropod activity in tropical anthropogenic forests
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 108 / Issue 6 / December 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 February 2018, pp. 792-799
-
- Article
- Export citation
Characterization of Semiconductor Materials Using Electron Holography
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 23 / Issue S1 / July 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 August 2017, pp. 1404-1405
- Print publication:
- July 2017
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Weed Suppression by Canola and Mustard Cultivars
-
- Journal:
- Weed Technology / Volume 22 / Issue 1 / March 2008
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 January 2017, pp. 182-185
-
- Article
- Export citation
Experimental study of flow around polygonal cylinders
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 812 / 10 February 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 December 2016, pp. 251-278
-
- Article
- Export citation
Intake of n-3 fatty acids and long-term outcome in renal transplant recipients: a post hoc analysis of a prospective cohort study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 116 / Issue 12 / 28 December 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 December 2016, pp. 2066-2073
- Print publication:
- 28 December 2016
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Chapter 15 - Goal-directed fluid therapy
- from Section 3 - Techniques
-
-
- Book:
- Clinical Fluid Therapy in the Perioperative Setting
- Published online:
- 05 June 2016
- Print publication:
- 26 May 2016, pp 110-119
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Late Saalian and Eemian deposits in the Amsterdam glacial basin
-
- Journal:
- Netherlands Journal of Geosciences / Volume 79 / Issue 2-3 / August 2000
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 April 2016, pp. 147-160
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Determination of Mean Inner Potential and Inelastic Mean Free Path of ZnTe Using Off-Axis Electron Holography and Dynamical Effects Affecting Phase Determination
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 21 / Issue 6 / December 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 November 2015, pp. 1406-1412
- Print publication:
- December 2015
-
- Article
- Export citation