Book contents
- Frontmatter
- Dedication
- Contents
- Preface
- 1 Introduction
- Part I Theory
- Part II Practice
- Part III Applications
- 13 Single-molecule biophysics
- 14 Cell biology
- 15 Spectroscopy
- 16 Optofluidics and lab-on-a-chip
- 17 Colloid science
- 18 Microchemistry
- 19 Aerosol science
- 20 Statistical physics
- 21 Nanothermodynamics
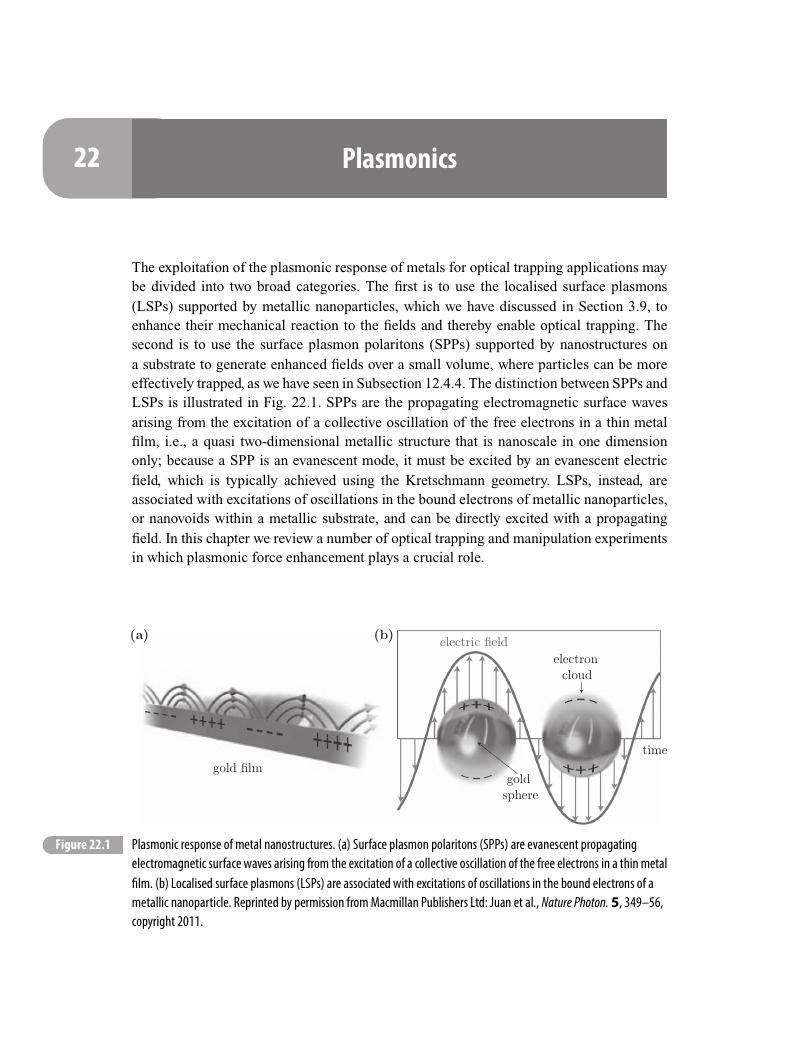
- 22 Plasmonics
- 23 Nanostructures
- 24 Laser cooling and trapping of atoms
- 25 Towards the quantum regime at the mesoscale
- Index
- References
22 - Plasmonics
from Part III - Applications
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 05 December 2015
- Frontmatter
- Dedication
- Contents
- Preface
- 1 Introduction
- Part I Theory
- Part II Practice
- Part III Applications
- 13 Single-molecule biophysics
- 14 Cell biology
- 15 Spectroscopy
- 16 Optofluidics and lab-on-a-chip
- 17 Colloid science
- 18 Microchemistry
- 19 Aerosol science
- 20 Statistical physics
- 21 Nanothermodynamics
- 22 Plasmonics
- 23 Nanostructures
- 24 Laser cooling and trapping of atoms
- 25 Towards the quantum regime at the mesoscale
- Index
- References
Summary
- Type
- Chapter
- Information
- Optical TweezersPrinciples and Applications, pp. 470 - 483Publisher: Cambridge University PressPrint publication year: 2015



