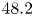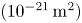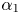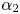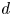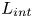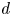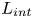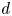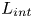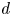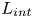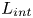281 results
CEO Cross-Sector Work Experience and Public–Private Partnership Formation of Private Firms in China
-
- Journal:
- Management and Organization Review , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 September 2024, pp. 1-30
-
- Article
- Export citation
Childhood socio-economic disadvantages versus adverse care experiences: Mediation and moderation impacts on late-life depressive symptoms
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 67 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 August 2024, e47
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
On incident shock wave/boundary layer interactions under the influence of expansion corner
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 988 / 10 June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 June 2024, A28
-
- Article
- Export citation
Anaesthesia management of interventional cardiac catheterisation for pulmonary atresia with intact ventricular septum and critical pulmonary stenosis: a retrospective analysis
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 May 2024, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
- Export citation
Spanwise unsteadiness in the sidewall-confined shock-wave/boundary-layer interaction
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 987 / 25 May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 May 2024, R6
-
- Article
- Export citation
Macrolide resistance of Mycoplasma pneumoniae in several regions of China from 2013 to 2019
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, e75
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mediterranean diet for cardiovascular disease: an evidence mapping study
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 27 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2024, e118
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The small heat shock protein Hsp20.8 imparts tolerance to high temperatures in the leafminer fly, Liriomyza trifolii (Diptera: Agtomyzidae)
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 114 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 March 2024, pp. 230-236
-
- Article
- Export citation
Cross-Section Measurements of the 11B(p,α)2α Reaction near the First Resonant Energy
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Delaminated and Pit-rich Nano-kaolinites obtained via an Intercalation-etching Method and their Application to Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 71 / Issue 4 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 448-460
-
- Article
- Export citation
Enhancement of Magnetic Vortex Acceleration by Laser Interaction with Near-Critical Density Plasma inside a Hollow Conical Target
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Compact Thomson Scattering Source Based on a Mixed Injection Assisted Laser Wakefield Accelerator
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The origins of saddles and riding technology in East Asia: discoveries from the Mongolian Altai
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Reevaluation of the protein requirement in Chinese elderly adults without sarcopenia with the indicator amino acid oxidation technique
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 8 / 28 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 December 2023, pp. 1377-1383
- Print publication:
- 28 April 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Inertial solution for high-pressure-difference pulse-decay measurement through microporous media
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 971 / 25 September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 September 2023, R1
-
- Article
- Export citation
How Surface-Level and Deep-Level Faultlines Influence Team Performance through Subgroup Formation and Team Interaction Quality: A Meta-analytic Review
-
- Journal:
- Management and Organization Review / Volume 19 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. 876-909
-
- Article
- Export citation
Elite chariots and early horse transport at the Bronze Age burial site of Shijia
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Separation length scaling for dual-incident shock wave–turbulent boundary layer interactions with different shock wave distances
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 960 / 10 April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 March 2023, A9
-
- Article
- Export citation