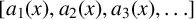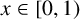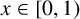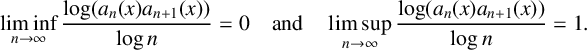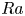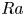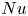392 results
On incident shock wave/boundary layer interactions under the influence of expansion corner
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 988 / 10 June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 June 2024, A28
-
- Article
- Export citation
Three-dimensional path planning with enhanced gravitational search algorithm for unmanned aerial vehicle
-
- Journal:
- Robotica , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 May 2024, pp. 1-35
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The long-term spatio-temporal trends in burden and attributable risk factors of major depressive disorder at global, regional and national levels during 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for GBD 2019
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 33 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 May 2024, e28
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Brightness enhancement on a narrow linewidth FBG-based MOPA fiber laser
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 May 2024, pp. 1-24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Prevalence of Nontuberculous Mycobacteria and the Emergence of Rare Species in Henan Province, China
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 May 2024, pp. 1-18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Global, regional and national burdens of depression in adolescents and young adults aged 10–24 years, from 1990 to 2019: findings from the 2019 Global Burden of Disease study
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry , FirstView
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 April 2024, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
- Export citation
Macrolide resistance of Mycoplasma pneumoniae in several regions of China from 2013 to 2019
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, e75
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
ASYMPTOTIC BEHAVIOUR FOR PRODUCTS OF CONSECUTIVE PARTIAL QUOTIENTS IN CONTINUED FRACTIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
- Export citation
Emergence of a hexagonal pattern in shear-thickening suspensions under orbital oscillations
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 984 / 10 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 April 2024, A69
-
- Article
- Export citation
Psychosocial and psychological interventions for schizophrenia relapse prevention: A bibliometric analysis
-
- Journal:
- Cambridge Prisms: Global Mental Health / Volume 11 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 April 2024, e49
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effectiveness of a WHO self-help psychological intervention to alleviate stress among healthcare workers in the context of COVID-19 in China: a randomised controlled trial
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 33 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 March 2024, e11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Enhanced heat transfer and reduced flow reversals in turbulent thermal convection with an obstructed centre
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 981 / 25 February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 February 2024, A16
-
- Article
- Export citation
Arazyme secreted by Serratia proteamaculans: current understanding in animal husbandry – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 161 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2024, p. 703
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Quantifying stakeholders’ preference for implantable medical devices in China: a discrete choice experiment
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care / Volume 40 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2024, e8
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Breast Cancer Prognosis Prediction and Immune Pathway Molecular Analysis Based on Mitochondria-Related Genes
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e56
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Tolerance of Clay Minerals by Cement: Effect of Side-Chain Density in Polyethylene Oxide (PEO) Superplasticizer Additives
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 64 / Issue 6 / December 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 732-742
-
- Article
- Export citation
Synthesis and Evaluation of Betaine Copolymer Filtrate Reducer for Drilling Mud
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 70 / Issue 2 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 252-269
-
- Article
- Export citation
Artificial Selection Drives SNPs of Olfactory Receptor Genes into Different Working Traits in Labrador Retrievers
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e77
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Identification of Key Biomarkers and Candidate Molecules in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer by Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e29
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation