No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Enhanced heat transfer and reduced flow reversals in turbulent thermal convection with an obstructed centre
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 21 February 2024
Abstract
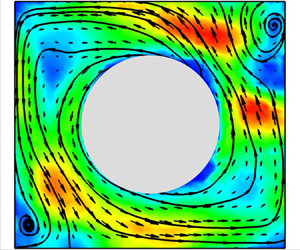
We report an experimental study about the effect of an obstructed centre on heat transport and flow reversal by inserting an adiabatic cylinder at the centre of a quasi-two-dimensional Rayleigh–Bénard convection cell. The experiments are carried out in a Rayleigh number ( $Ra$) range of
$Ra$) range of  $2\times 10^7 \leq Ra \leq 2\times 10^9$ and at a Prandtl number (
$2\times 10^7 \leq Ra \leq 2\times 10^9$ and at a Prandtl number ( $Pr$) of
$Pr$) of  $5.7$. It is found that for low
$5.7$. It is found that for low  $Ra$, the obstructed centre leads to a heat transfer enhancement of up to 21
$Ra$, the obstructed centre leads to a heat transfer enhancement of up to 21  $\%$, while as
$\%$, while as  $Ra$ increases, the magnitude of the heat transfer enhancement decreases and the heat transfer efficiency (
$Ra$ increases, the magnitude of the heat transfer enhancement decreases and the heat transfer efficiency ( $Nu$) eventually converges to that of the unobstructed normal cell. Particle image velocimetry measurements show that the heat transfer enhancement originates from the change in flow topology due to the presence of the cylindrical obstruction. In the low-
$Nu$) eventually converges to that of the unobstructed normal cell. Particle image velocimetry measurements show that the heat transfer enhancement originates from the change in flow topology due to the presence of the cylindrical obstruction. In the low- $Ra$ regime the presence of the obstruction promotes the transition of the flow topology from the four-roll state to the abnormal single-roll state then to the normal single-roll state with increasing obstruction size. While in the high-
$Ra$ regime the presence of the obstruction promotes the transition of the flow topology from the four-roll state to the abnormal single-roll state then to the normal single-roll state with increasing obstruction size. While in the high- $Ra$ regime, the flow is always in the single-roll state regardless of the obstruction size, although the flow becomes more coherent with the size of the obstruction. We also found that in the presence of the cylindrical obstruction, the stability of the corner vortices is significantly reduced, leading to a large reduction in the frequency of flow reversals.
$Ra$ regime, the flow is always in the single-roll state regardless of the obstruction size, although the flow becomes more coherent with the size of the obstruction. We also found that in the presence of the cylindrical obstruction, the stability of the corner vortices is significantly reduced, leading to a large reduction in the frequency of flow reversals.
JFM classification
- Type
- JFM Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2024. Published by Cambridge University Press





