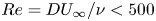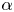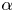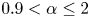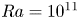98 results
Cross-sectional Relationship Between Dietary Protein Intake, Energy Intake and Protein Energy Wasting in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 May 2024, pp. 1-18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The long-term spatio-temporal trends in burden and attributable risk factors of major depressive disorder at global, regional and national levels during 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for GBD 2019
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 33 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 May 2024, e28
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Shape effect on solid melting in flowing liquid
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 980 / 10 February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 January 2024, R1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Cross-Section Measurements of the 11B(p,α)2α Reaction near the First Resonant Energy
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Association between the PLTP rs4810479 SNP and Serum Lipid Traits in the Chinese Maonan and Han Populations
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2021 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e14
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Enhancement of Magnetic Vortex Acceleration by Laser Interaction with Near-Critical Density Plasma inside a Hollow Conical Target
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Charge State of Protons with 90 and 100 keV Energies Decelerated in Hydrogen Plasma
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2021 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Live birth rate of gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonist versus luteal phase gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist protocol in IVF/ICSI: a systematic review and meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine / Volume 26 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 December 2023, e2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Reevaluation of the protein requirement in Chinese elderly adults without sarcopenia with the indicator amino acid oxidation technique
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 8 / 28 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 December 2023, pp. 1377-1383
- Print publication:
- 28 April 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Characterization of the complete mitochondrial genomes of the zoonotic parasites Bolbosoma nipponicum and Corynosoma villosum (Acanthocephala: Polymorphida) and the molecular phylogeny of the order Polymorphida
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 151 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 November 2023, pp. 45-57
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Numerical analyses of the flow past a short rotating cylinder
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 975 / 25 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 November 2023, A15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
“On the Centre–Periphery Borderline”: Educational Studies on/in Mainland China in the Global Context
-
- Journal:
- The China Quarterly / Volume 258 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 October 2023, pp. 548-558
- Print publication:
- June 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Demonstration of a diode-pumped dual-wavelength metastable krypton laser
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 September 2023, e87
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Ice melting in salty water: layering and non-monotonic dependence on the mean salinity
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 969 / 25 August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 August 2023, R2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Using molecular network analysis to understand current HIV-1 transmission characteristics in an inland area of Yunnan, China
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 July 2023, e124
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Morphology evolution of a melting solid layer above its melt heated from below
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 956 / 10 February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 February 2023, A23
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Bilingual interactional contexts predict executive functions in older adults
-
- Journal:
- Bilingualism: Language and Cognition / Volume 26 / Issue 1 / January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2022, pp. 36-47
-
- Article
- Export citation