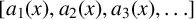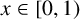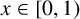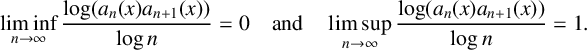309 results
Clay and Fe (oxyhydr)oxide mineralogy in the basalt weathering profile in Hainan (southern China): implications for pedogenesis process
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 72 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 July 2024, e8
-
- Article
- Export citation
Modelling the first droplet emission from an electrified liquid meniscus hanging at the nozzle tip
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 987 / 25 May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 May 2024, A38
-
- Article
- Export citation
ASYMPTOTIC BEHAVIOUR FOR PRODUCTS OF CONSECUTIVE PARTIAL QUOTIENTS IN CONTINUED FRACTIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effects of retrieval schedules on the acquisition of explicit, automatized-explicit, and implicit knowledge of L2 collocations
-
- Journal:
- Studies in Second Language Acquisition , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 April 2024, pp. 1-23
-
- Article
- Export citation
Mood disorders influencing endometriosis and adenomyosis: Mendelian randomisation study
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 10 / Issue 3 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2024, e83
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effect of vegetable consumption on risk of gastric cancer: a systematic review and multi-level meta-analysis of prospective studies
-
- Journal:
- Nutrition Research Reviews , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 February 2024, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
- Export citation
FC1: Effect of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS) on Left Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex (DLPFC) in Dementia with Lewy Bodies (DLB)
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 35 / Issue S1 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2024, pp. 64-65
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
FC2: The effect of Maintenance phase of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS) in Alzheimer’s Dementia
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 35 / Issue S1 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2024, pp. 65-66
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Depression, anxiety and brain volume after hearing loss and tinnitus: cohort study in the UK Biobank
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 10 / Issue 2 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 February 2024, e37
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Peer review of clinical and translational research manuscripts: Perspectives from statistical collaborators
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 January 2024, e20
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Comprehensive Multiomics Analysis of Monozygotic Twin Discordant for Double Outlet Right Ventricle
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 26 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 December 2023, pp. 370-378
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mapping the global, regional and national burden of bipolar disorder from 1990 to 2019: trend analysis on the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 224 / Issue 2 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 December 2023, pp. 36-46
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dual-band transmissive linear to circular polarization converter with angular-stable and orthogonal polarizations
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 December 2023, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
- Export citation
Revealing the psychopathological pathway linking trauma to post-traumatic stress disorder: longitudinal network approach
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 10 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 December 2023, e2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Postmarket safety profile of suicide/self-injury for GLP-1 receptor agonist: a real-world pharmacovigilance analysis
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 November 2023, e99
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Gray matter atrophy is constrained by normal structural brain network architecture in depression
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 7 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2023, pp. 1318-1328
-
- Article
- Export citation
A 24-year longitudinal study of Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from patients with bacteraemia and urinary tract infections reveals the association between capsular serotypes, antibiotic resistance, and virulence gene distribution
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 September 2023, e155
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Zoonotic pathogens identified in rodents and shrews from four provinces, China, 2015–2022
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 September 2023, e174
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Uncovering key clinical trial features influencing recruitment
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 7 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 September 2023, e199
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation