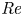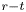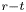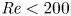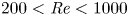77 results
Unifying constitutive law of vibroconvective turbulence in microgravity
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 987 / 25 May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 May 2024, A14
-
- Article
- Export citation
Unraveling the link between childhood maltreatment and depression: Insights from the role of ventral striatum and middle cingulate cortex in hedonic experience and emotion regulation
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2024, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
- Export citation
Formation of H3O+ in the Ionization and Fragmentation of Ethanol Induced by Electron Beam Irradiation
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2021 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e23
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effects of Dietary Palygorskite Supplementation on Cecal Microbial Community Structure and the Abundance of Antibiotic-Resistant Genes in Broiler Chickens Fed With Chlortetracycline
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 69 / Issue 2 / April 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 205-216
-
- Article
- Export citation
Enhancement of Magnetic Vortex Acceleration by Laser Interaction with Near-Critical Density Plasma inside a Hollow Conical Target
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Evaluation Of Zinc-Bearing Palygorskite Effects on Growth Performance, Nutrient Retention, Meat Quality, and Zinc Accumulation in Blunt Snout Bream Megalobrama Amblycephala
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 66 / Issue 3 / June 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 274-285
-
- Article
- Export citation
Tuning the Acidity of Montmorillonite by H3PO4-Activation and Supporting WO3 for Catalytic Dehydration of Glycerol to Acrolein
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 70 / Issue 3 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 460-479
-
- Article
- Export citation
An Evaluation of the Supplementation of Dietary-Modified Palygorskite on Growth Performance, Zearalenone Residue, Serum Metabolites, and Antioxidant Capacities in Broilers Fed a Zearalenone-Contaminated Diet
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 66 / Issue 6 / December 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 474-484
-
- Article
- Export citation
Prospect of ultrahigh-resolution fast neutron absorption spectroscopy based on a laser plasma electron accelerator
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 12 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 November 2023, e11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Interactions between oblique second mode and oblique waves in a high-speed boundary layer
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 973 / 25 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 October 2023, A27
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dual-stage radial–tangential vortex tilting reverses radial vorticity and contributes to leading-edge vortex stability on revolving wings
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 963 / 25 May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 May 2023, A29
-
- Article
- Export citation
Power Transmission Network Optimization Strategy Based on Random Fractal Beetle Antenna Algorithm
-
- Journal:
- Wireless Power Transfer / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e1
- Print publication:
- 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Vibration-induced ‘anti-gravity’ tames thermal turbulence at high Rayleigh numbers
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 951 / 25 November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 November 2022, A13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Control of oblique breakdown in a supersonic boundary layer employing a local cooling strip
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 949 / 25 October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 September 2022, A4
-
- Article
- Export citation
“I no longer count in German.” On dominance shift in returnee heritage speakers
-
- Journal:
- Applied Psycholinguistics / Volume 43 / Issue 5 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 September 2022, pp. 1019-1043
-
- Article
- Export citation
Suppression of flow reversals via manipulating corner rolls in plane Rayleigh–Bénard convection
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 946 / 10 September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 August 2022, A44
-
- Article
- Export citation
Multiple molecular characteristics of circulating enterovirus types among paediatric hand, foot and mouth disease patients after EV71 vaccination campaign in Wuxi, China
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 April 2022, e98
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effects of Reynolds number on leading-edge vortex formation dynamics and stability in revolving wings
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 931 / 25 January 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 November 2021, A13
-
- Article
- Export citation
Altered intrinsic default mode network functional connectivity in patients with remitted geriatric depression and amnestic mild cognitive impairment
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 34 / Issue 8 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 October 2021, pp. 703-714
-
- Article
- Export citation