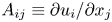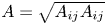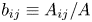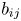735 results

Inside the IPCC
- How Assessment Practices Shape Climate Knowledge
-
- Published online:
- 03 June 2024
- Print publication:
- 20 June 2024
-
- Element
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
GR.6 Meningioma molecular classification predicts response to surgery and adjuvant radiotherapy: an integrated clinicomolecular analysis & prospective validation
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 51 / Issue s1 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 May 2024, p. S2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Physiological and biochemical processes underlying the differential sucrose yield and biomass production in sugarcane varieties
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Agriculture / Volume 60 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 May 2024, e13
-
- Article
- Export citation
Comment on: Fürsich et al., 2023, Miocene instead of Jurassic: the importance of sound fieldwork for paleontological data analysis
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Paleontology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 April 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
- Export citation
Data-driven model for Lagrangian evolution of velocity gradients in incompressible turbulent flows
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 984 / 10 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 April 2024, A39
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Inequality on the frontline: A multi-country study on gender differences in mental health among healthcare workers during the COVID-19 pandemic
-
- Journal:
- Cambridge Prisms: Global Mental Health / Volume 11 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 March 2024, e34
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Self-Organized Inorganic-Organic Hybrids Induced by Silylating Agents with Phyllosilicate-Like Structure and the Influence of the Adsorption of Cations
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 48 / Issue 6 / December 2000
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 638-647
-
- Article
- Export citation
Quantification and Characterization of Maghemite in Soils Derived from Volcanic Rocks in Southern Brazil
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 47 / Issue 4 / August 1999
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 466-473
-
- Article
- Export citation
Alteration of Ilmenite in the Manavalakurichi Deposit, India
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 42 / Issue 5 / October 1994
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 567-571
-
- Article
- Export citation
Somatic multicomorbidity and disability in patients with psychiatric disorders in comparison to the general population: a quasi-epidemiological investigation in 54,826 subjects from 40 countries (COMET-G study)
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 29 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2024, pp. 126-149
-
- Article
- Export citation
Mineralogical, Chemical, and Physical Characterization of Synthetic Al-Substituted Maghemites (γ−Fe2−xAlxO3)
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 58 / Issue 4 / August 2010
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 451-461
-
- Article
- Export citation
Genetic diversity and population structure analysis in early generations maize inbreds derived from local germplasm of Eastern Himalayan regions using microsatellite markers
-
- Journal:
- Plant Genetic Resources / Volume 21 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 November 2023, pp. 418-425
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effect of external magnetic field and dust grains on the properties of ion-acoustic waves
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 89 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 September 2023, 905890502
-
- Article
- Export citation
Rice genetic resources for organic agriculture under hill ecology: evaluation and usefulness
-
- Journal:
- Plant Genetic Resources / Volume 21 / Issue 2 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 August 2023, pp. 159-165
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effect of the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet on the development of preeclampsia and metabolic outcomes in pregnant women with pre-existing diabetes mellitus: a randomized, controlled, single-blind trial – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Nutritional Science / Volume 12 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 July 2023, e88
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Psychosocial effects of the covid-19 lockdown`s on school-age childrens: A literature review
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S803-S804
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
DELUSION OF PREGNANCY IN PATIENT WITH MAJOR NEUROCOGNITIVE DISORDER: A CASE REPORT
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S939-S940
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Adjunctive Therapy of Text4Support for Treatment-Resistant Depression Patients Receiving Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation. A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Pilot Trial
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S838
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Effect of the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet on the development of preeclampsia and metabolic outcomes in pregnant women with pre-existing diabetes mellitus: a randomised, controlled, single-blind trial
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Nutritional Science / Volume 12 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 July 2023, e73
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
P.017 Convergent and contrasting modulation of saccade and pupil responses by several neurodegenerative diseases during free viewing of video clips
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 50 / Issue s2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2023, p. S62
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation