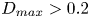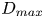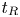222 results
Resistance patterns and molecular basis to ACCase-inhibiting herbicides
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science , FirstView
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 May 2024, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
- Export citation
Status and influencing factors of nurses’ burnout: A cross-sectional study during COVID-19 regular prevention and control in Jiangsu Province, China
-
- Journal:
- Cambridge Prisms: Global Mental Health / Volume 11 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2024, e54
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Non-linear relationship between the body roundness index and metabolic syndrome: data from National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 1999–2018
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 11 / 14 June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 February 2024, pp. 1852-1859
- Print publication:
- 14 June 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Design of dual-band tunable bandpass filter with constant absolute bandwidth based on triple transmission path
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 February 2024, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
- Export citation
Impact of primary care triage using the Head and Neck Cancer Risk Calculator version 2 on tertiary head and neck services in the post-coronavirus disease 2019 period
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 January 2024, pp. 1-6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Rabies vaccination adherence and associated factors among rabies-exposed patients in Shenzhen, China: a hospital-based cross-sectional study
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 January 2024, e15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Clay Mineralogy of Surface Sediments in the Three Gorges Reservoir: Implications for Sediment Provenances and Weathering Regimes
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 69 / Issue 1 / February 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 52-67
-
- Article
- Export citation
Removal of Reactive Brilliant Orange X-GN from Aqueous Solutions By Mg-Al Layered Double Hydroxides
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 59 / Issue 5 / October 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 438-445
-
- Article
- Export citation
17 The Chinese Version of Craft Story Recall: A Preliminary Study on the Diagnostic Values of Mild Cognitive Impairment and Dementia.
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 700-701
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Upregulation of miR-21-5p rescues the inhibition of cardiomyocyte proliferation induced by high glucose through negative regulation of Rhob
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease / Volume 14 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 December 2023, pp. 670-677
-
- Article
- Export citation
Two-dimensional Janus drops in shear: deformation, rotation and their coupling
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 976 / 10 December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 December 2023, A29
-
- Article
- Export citation
Determination of suitable reference genes for RT-qPCR normalisation in Bombyx mori (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae) infected by the parasitoid Exorista sorbillans (Diptera, Tachinidae)
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 113 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 November 2023, pp. 845-857
-
- Article
- Export citation
Gray matter atrophy is constrained by normal structural brain network architecture in depression
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 7 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2023, pp. 1318-1328
-
- Article
- Export citation
Microstructural observations of clay-hosted pores in black shales: implications for porosity preservation and petrophysical variability
-
- Journal:
- Clay Minerals / Volume 58 / Issue 3 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 October 2023, pp. 310-323
-
- Article
- Export citation
Clinical characteristics of 1279 patients with hepatitis E in Tianjin
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 September 2023, e157
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Probability or time: Effect of presentation format on continuous risky decisions
-
- Journal:
- Judgment and Decision Making / Volume 18 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 August 2023, e26
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Germination ecology and response to herbicides of Ludwigia prostrata and their implication for weed control in paddy fields
-
- Journal:
- Weed Technology / Volume 37 / Issue 2 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 May 2023, pp. 197-204
-
- Article
- Export citation
Roles of obesity in mediating the causal effect of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder on diabetes
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 32 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 May 2023, e32
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation