45 results
The associations of dietary intake of high sodium and low zinc with gastric cancer mortality: a prospective cohort study in South Korea
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 82 / Issue OCE1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 March 2023, E18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
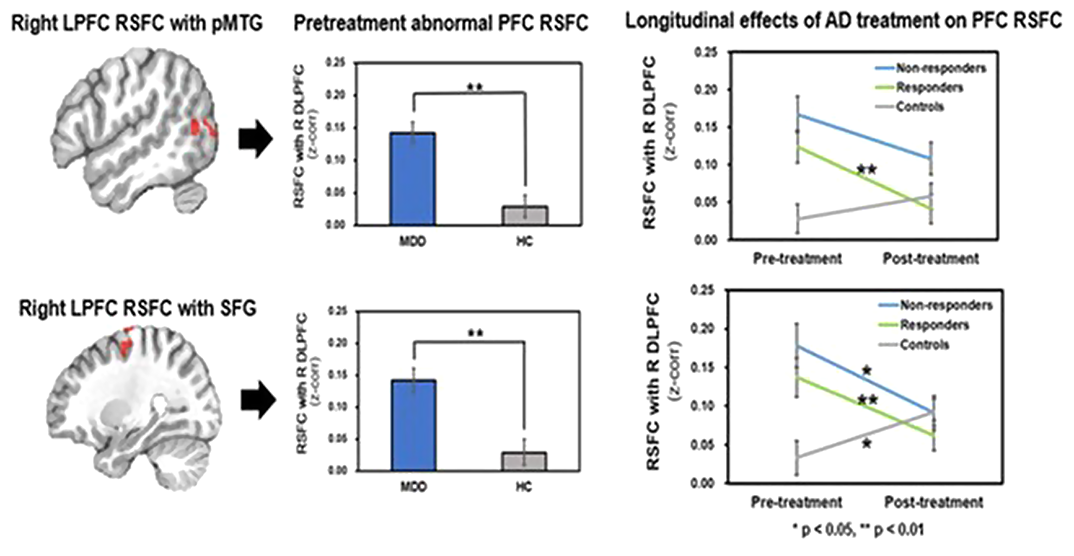
Longitudinal effects of antidepressant treatment on resting state functional connectivity in adolescents with major depressive disorder
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 65 / Issue S1 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 September 2022, p. S85
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Amygdala responses to threat in violence-exposed children depend on trauma context and maternal caregiving
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology / Volume 35 / Issue 3 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 October 2021, pp. 1159-1170
-
- Article
- Export citation
Harm Avoidance as an Endophenotype of Schizophrenia: Comparative Study of First-degree Relatives, Schizophrenia Probands, and Healthy Controls
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 24 / Issue S1 / January 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2020, 24-E1199
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
2649 – White Matter Hyperintensities are an Independent Predictor of Future Depressive Disorders: 3-Year Results from Epidemiological Study of Vascular Depression in Korean Elderly
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2020, 28-E1566
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Paternal Smoking During Early Developmental Period and Risk of Offspring's Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 41 / Issue S1 / April 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 March 2020, p. S220
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Palatable Food Access During Adolescence Increased BDNF Expression in the Nucleus Accumbens and Anxiety-/Depression-Like Behaviors in Males, But Not in Females
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 41 / Issue S1 / April 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 March 2020, p. S284
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Korean medication algorithm for depressive disorder (KMAP-DD) 2017: Maintenance treatment
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 41 / Issue S1 / April 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 March 2020, p. S530
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Efficacy and safety of generic escitalopram (Lexacure) in patients with major depressive disorder: A 6-week, multi-center, randomized, rater-blinded, escitalopram-comparative, non-inferiority study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 33 / Issue S1 / March 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 March 2020, p. s227
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Blonanserin augmentation in patients with schizophrenia – who is benefited from blonanserin augmentation?: An open-label, prospective, multicenter study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 33 / Issue S1 / March 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 March 2020, p. s226
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Chronic methiopropamine modifies preference of choice in rat gambling task
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 41 / Issue S1 / April 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 March 2020, pp. s866-s867
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Integrated one-dimensional dynamic analysis methodology for space launch vehicles reflecting liquid components
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 121 / Issue 1243 / September 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 July 2017, pp. 1217-1238
-
- Article
- Export citation
Spectral tomographic analysis of Bremsstrahlung X-rays generated in a laser-produced plasma
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 34 / Issue 4 / December 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2016, pp. 645-654
-
- Article
- Export citation
Reduction of nitrogen excretion and emissions from poultry: a review for conventional poultry
-
- Journal:
- World's Poultry Science Journal / Volume 72 / Issue 3 / September 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 August 2016, pp. 509-520
- Print publication:
- September 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
Microstructural characteristics of GaN/AlN thin films grown on a Si (110) substrate by molecular beam epitaxy: Transmission electron microscopy study
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 22 / Issue S3 / July 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 July 2016, pp. 1576-1577
- Print publication:
- July 2016
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Characterization of Defects in III-V Semiconductor Materials (InP, GaAs and InGaAs/ InP on Si) in Nano-sized Patterns by Transmission Electron Microscopy
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 22 / Issue S3 / July 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 July 2016, pp. 1540-1541
- Print publication:
- July 2016
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Interplay of Octahedral Rotations, Magnetic and Electronic Properties in Epitaxial LaCoO3 Thin Films
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 19 / Issue S2 / August 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 October 2013, pp. 1924-1925
- Print publication:
- August 2013
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
(A85) Analysis of Health Risk Perception and Behavior Changes during Elevated Temperatures for an Urban Chinese Population
-
- Journal:
- Prehospital and Disaster Medicine / Volume 26 / Issue S1 / May 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 May 2011, p. s24
- Print publication:
- May 2011
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Introduction to AMUSES: AKARI survey with a window of opportunity
-
- Journal:
- European Astronomical Society Publications Series / Volume 46 / 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 March 2011, pp. 149-154
- Print publication:
- 2011
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Enhancement of plasticity in Ti-based metallic glass matrix composites by controlling characteristic and volume fraction of primary phase
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 25 / Issue 11 / November 2010
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2011, pp. 2183-2191
- Print publication:
- November 2010
-
- Article
- Export citation