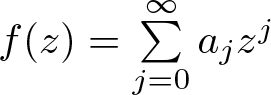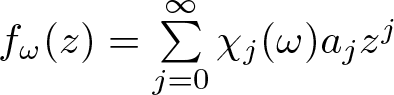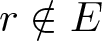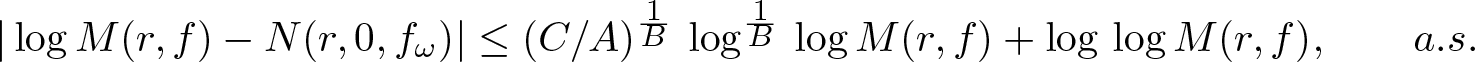45 results
Dispersion and Swellability of Ternary Surfactant Co-Modified Montmorillonites
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 69 / Issue 6 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 759-771
-
- Article
- Export citation
TPX2 Serves as a Cancer Susceptibility Gene and Is Closely Associated with the Poor Prognosis of Endometrial Cancer
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e70
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Comprehensive Multiomics Analysis of Monozygotic Twin Discordant for Double Outlet Right Ventricle
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 26 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 December 2023, pp. 370-378
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Inequalities concerning maximum modulus and zeros of random entire functions
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 67 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 October 2023, pp. 57-78
-
- Article
- Export citation
The complete mitochondrial genome of Ogmocotyle ailuri: gene content, composition and rearrangement and phylogenetic implications
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 150 / Issue 8 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 April 2023, pp. 661-671
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Growth, development, and host preference of Histiostoma feroniarum (Acaridida: Histiostomatidae): effects of temperature and types of mushroom cultivar
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 113 / Issue 3 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 March 2023, pp. 412-418
-
- Article
- Export citation
The global disease burden attributable to a diet low in fibre in 204 countries and territories from 1990 to 2019
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 26 / Issue 4 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 September 2022, pp. 854-865
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Geometric morphometric analysis for the systematic elucidation of new Hylicellidae from the Jurassic of China (Hemiptera: Cicadomorpha)
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Paleontology / Volume 96 / Issue 5 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 May 2022, pp. 1119-1131
-
- Article
- Export citation
Compressed sensorimotor-to-transmodal hierarchical organization in schizophrenia
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 3 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 June 2021, pp. 771-784
-
- Article
- Export citation
The influence of pre-existing hypertension on coronavirus disease 2019 patients
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 149 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2021, e4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The association of the glucokinase rs4607517 polymorphism with gestational diabetes mellitus and its interaction with sweets consumption in Chinese women
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 24 / Issue 9 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 June 2020, pp. 2563-2569
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Associations of fat and carbohydrate intake with becoming overweight and obese: an 11-year longitudinal cohort study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 124 / Issue 7 / 14 October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 May 2020, pp. 715-728
- Print publication:
- 14 October 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effects of dietary inulin supplementation on growth performance, intestinal barrier integrity and microbial populations in weaned pigs
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 124 / Issue 3 / 14 August 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2020, pp. 296-305
- Print publication:
- 14 August 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
A brief review of data-driven ICME for intelligently discovering advanced structural metal materials: Insight into atomic and electronic building blocks
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 8 / 28 April 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2020, pp. 872-889
- Print publication:
- 28 April 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The kinetic Shakhov–Enskog model for non-equilibrium flow of dense gases
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 883 / 25 January 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 November 2019, A48
-
- Article
- Export citation
Malnutrition screening and acute kidney injury in hospitalised patients: a retrospective study over a 5-year period from China
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 123 / Issue 3 / 14 February 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2019, pp. 337-346
- Print publication:
- 14 February 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Serum folate concentrations at diagnosis are associated with hepatocellular carcinoma survival in the Guangdong Liver Cancer Cohort study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 121 / Issue 12 / 28 June 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 June 2019, pp. 1376-1388
- Print publication:
- 28 June 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Brief cognitive–behavioural therapy for patients in the community with schizophrenia: Randomised controlled trial in Beijing, China – RETRACTION
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 215 / Issue 1 / July 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 May 2019, p. 435
- Print publication:
- July 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Underground nuclear astrophysics experiment JUNA in China
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 15 / Issue S350 / April 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 October 2020, pp. 313-320
- Print publication:
- April 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation