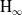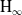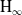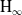5973 results
A retrospective analysis of iv ketamine outcome on hospitalizations in an unselected psychiatric sample
-
- Journal:
- Acta Neuropsychiatrica / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 April 2024, pp. 1-21
-
- Article
- Export citation
Workflow and Outcome of Thrombectomy in Late Time Window. A Pooled Multicenter Analysis
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 April 2024, pp. 1-18
-
- Article
- Export citation
Frequency-dependent
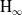 $\textrm{H}_{{\infty }}$ control for wind disturbance rejection of a fully actuated UAV
$\textrm{H}_{{\infty }}$ control for wind disturbance rejection of a fully actuated UAV
-
- Journal:
- Robotica , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2024, pp. 1-15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mixed-Layer Illite/Smectite Minerals in Tertiary Sandstones and Shales, San Joaquin Basin, California
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 34 / Issue 2 / April 1986
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, pp. 115-124
-
- Article
- Export citation
David Zimmerman, Ensnared between Hitler and Stalin: Refugee Scientists in the USSR Toronto: University of Toronto Press, 2023. Pp. 376. ISBN 978-1-4875-4365-5. $85.00 (hardcover).
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal for the History of Science , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 March 2024, pp. 1-3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Atypical Bilateral Idiopathic Inflammatory Cavernous Sinus Syndrome Responsive to Cyclophosphamide
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 March 2024, pp. 1-3
-
- Article
- Export citation
Palagonite Reconsidered: Paracrystalline Illite-Smectites From Regoliths on Basic Pyroclastics
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 42 / Issue 5 / October 1994
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 582-592
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effect of Permo-Carboniferous Climate on Illite-Smectite, Haushi Group, Sultanate of Oman
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 47 / Issue 2 / April 1999
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 131-143
-
- Article
- Export citation
Range extension of invasive Cancer irroratus and native Carcinus maenas polewards in the Ascophyllum-dominated intertidal zone in north-west Iceland
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom / Volume 104 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 February 2024, e3
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Italian Opera Singers in Mozart's Vienna Dorothea Link Urbana: University of Illinois Press, 2022 pp. viii + 484, IBSN 978 0 252 04464 9
-
- Journal:
- Eighteenth-Century Music / Volume 21 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 February 2024, pp. 75-77
- Print publication:
- March 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Research agenda for antibiotic stewardship within the Veterans’ Health Administration, 2024–2028
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2024, pp. 1-7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Rare cardiac tumour-nodular fasciitis
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 4 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2024, pp. 933-934
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
CONNECTing Concussion Care with Research Across Ontario
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 January 2024, pp. 1-5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Larsson, Remade: A Computational Perspective on the Millennium Trilogy in English
-
- Journal:
- PMLA / Publications of the Modern Language Association of America / Volume 139 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 April 2024, pp. 82-96
- Print publication:
- January 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Granting Immigrants the Right to Vote in National Elections: Empirical Evidence from Swedish Administrative Data
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Political Science , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 December 2023, pp. 1-18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
30 Examining the Base Rates of Low Scores in Older Adults with Subjective Cognitive Impairment from a Specialist Memory Clinic
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 711-712
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Distortions in focusing laser pulses due to spatio-temporal couplings–An analytic description
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 December 2023, pp. 1-34
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
A deep new look at color
-
- Journal:
- Behavioral and Brain Sciences / Volume 46 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 December 2023, e389
-
- Article
- Export citation
2 - Targeting Private Sector Influence in Politics
- from Section I - Foundations of Corporate Political Responsibility: Metrics for Disclosure and Good Governance
-
-
- Book:
- Corporate Political Responsibility
- Published online:
- 16 November 2023
- Print publication:
- 30 November 2023, pp 30-61
-
- Chapter
- Export citation