400 results
Impact of total parenteral nutrition versus exclusive enteral nutrition on postoperative adverse outcomes in patients with penetrating Crohn’s disease undergoing surgical resection: A retrospective cohort study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 June 2024, pp. 1-28
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Emergence of a hexagonal pattern in shear-thickening suspensions under orbital oscillations
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 984 / 10 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 April 2024, A69
-
- Article
- Export citation
Psychosocial and psychological interventions for schizophrenia relapse prevention: A bibliometric analysis
-
- Journal:
- Cambridge Prisms: Global Mental Health / Volume 11 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 April 2024, e49
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Longitudinal association between soft drink consumption and handgrip strength in adults: a prospective analysis from the Tianjin Chronic Low-Grade Systemic Inflammation and Health (TCLSIH) cohort study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 12 / 28 June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2024, pp. 1997-2004
- Print publication:
- 28 June 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Variation of millet grain size and cooking techniques across Asia between the late fourth and first millennia BC
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Application of computer vision and deep learning models to automatically classify medically important mosquitoes in North Borneo, Malaysia
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 114 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 April 2024, pp. 302-307
-
- Article
- Export citation
Depression, anxiety and brain volume after hearing loss and tinnitus: cohort study in the UK Biobank
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 10 / Issue 2 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 February 2024, e37
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
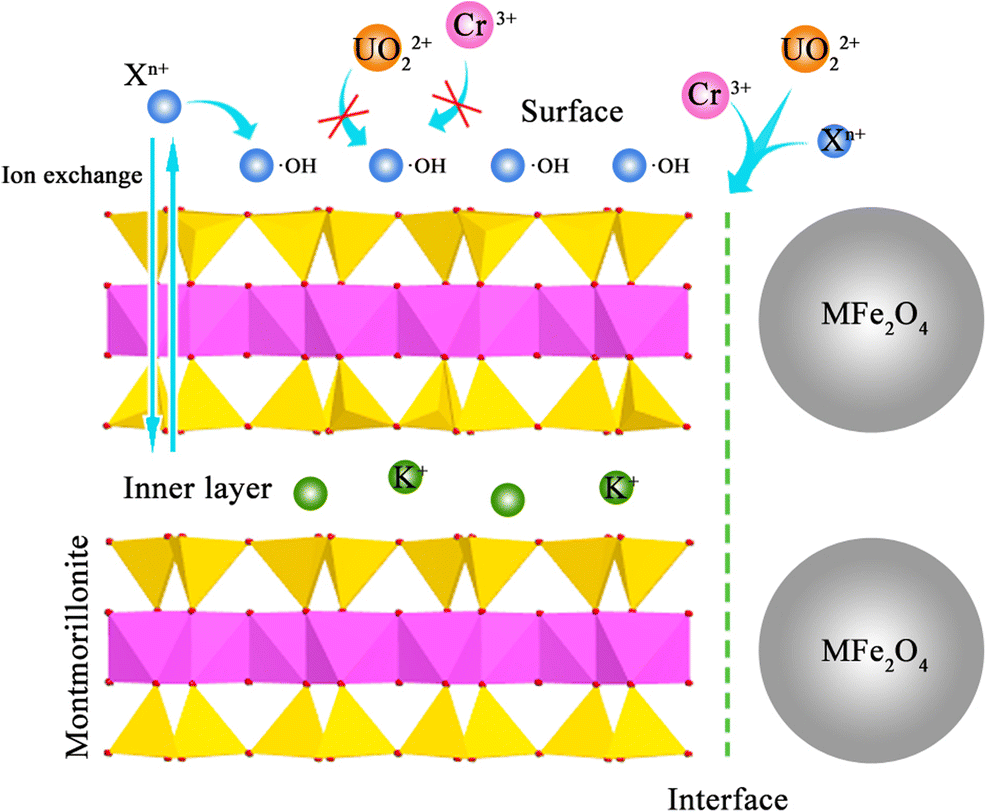
Competitive Adsorption of Uranyl and Toxic Trace Metal Ions at MFe2O4-montmorillonite (M = Mn, Fe, Zn, Co, or Ni) Interfaces
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 67 / Issue 4 / August 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 291-305
-
- Article
- Export citation
Novel KDM2B/SAV1 Signaling Pathway Promotes the Progression of Gastric Cancer
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
An Axial Foilless Diode Guided by Composite Magnetic Field for the Production of Relativistic Electron Beams
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2021 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e16
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Multiple Hierarchical Heterojunction g-C3N4/LDH/Ag3PO4 With Enhanced Visible-Light Photocatalytic Activity for Cr(Vi) Reduction
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 69 / Issue 2 / April 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 243-253
-
- Article
- Export citation
The egg ribonuclease SjCP1412 accelerates liver fibrosis caused by Schistosoma japonicum infection involving damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs)
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 151 / Issue 3 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 December 2023, pp. 260-270
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mapping the global, regional and national burden of bipolar disorder from 1990 to 2019: trend analysis on the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 224 / Issue 2 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 December 2023, pp. 36-46
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Digital generation of super-Gaussian perfect vortex beams via wavefront shaping with globally adaptive feedback
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 12 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 November 2023, e5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Generation of energetic electrons by an electron cyclotron wave through stochastic heating in a spherical tokamak
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 89 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 November 2023, 905890603
-
- Article
- Export citation
Anatomical studies and early results on endoscopic transoral medial pterygomandibular fold approach to salvage retropharyngeal lymphadenectomy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 138 / Issue 5 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 November 2023, pp. 540-547
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Genesis of the Jinying gold deposit, southern Jilin Province, NE China: Constraints from geochronology and isotope geochemistry
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 160 / Issue 9 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 November 2023, pp. 1761-1774
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Multi-locus phylogeny of Bryoria reveals recent diversification and unexpected diversity in section Divaricatae
-
- Journal:
- The Lichenologist / Volume 55 / Issue 6 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 November 2023, pp. 497-517
- Print publication:
- November 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
How are policy pilots managed? Findings from the New Rural Cooperative Medical Scheme in China
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Public Policy / Volume 44 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2023, pp. 143-163
-
- Article
- Export citation
Nuclear DNA-based phylogenetic analysis of Neocinnamomum species
-
- Journal:
- Plant Genetic Resources / Volume 21 / Issue 4 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 October 2023, pp. 323-330
-
- Article
- Export citation