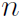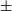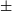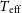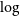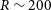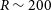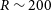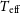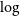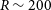177 results
LIMIT COMPLEXITIES, MINIMAL DESCRIPTIONS, AND
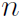 $n$-RANDOMNESS
$n$-RANDOMNESS
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Symbolic Logic / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2024, pp. 1-16
-
- Article
- Export citation
Complete mitochondrial genome of Scathophaga stercoraria (Diptera: Scathophagidae) in wild plateau pika: Genome descriptions and Phylogenetic evolution
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 May 2024, pp. 1-27
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
A meta-analysis comparing the efficacy and safety of different modes of administration of cream in the treatment of otomycosis
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 May 2024, pp. 1-26
-
- Article
- Export citation
Longitudinal association between soft drink consumption and handgrip strength in adults: a prospective analysis from the Tianjin Chronic Low-Grade Systemic Inflammation and Health (TCLSIH) cohort study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 12 / 28 June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2024, pp. 1997-2004
- Print publication:
- 28 June 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Subconvective wall-pressure fluctuations in low-Mach-number turbulent channel flow
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 984 / 10 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 April 2024, R2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Deblending overlapping galaxies in DECaLS using transformer-based algorithm: A method combining multiple bands and data types
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 41 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 March 2024, e035
-
- Article
- Export citation
An acceleration method employing sparse sensing matrix for fast analysis of the wide-angle electromagnetic problems based on compressive sensing
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 March 2024, pp. 1-6
-
- Article
- Export citation
Breast Cancer Prognosis Prediction and Immune Pathway Molecular Analysis Based on Mitochondria-Related Genes
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e56
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Sodium Polyacrylate-Modified Bentonite and Its Dehydration Testing in Real Oil
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 70 / Issue 2 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 290-304
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Estimating stellar parameters and identifying very metal-poor stars for low-resolution spectra (R ∼ 200)
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 41 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 November 2023, e002
-
- Article
- Export citation
Research trends in mental health problems of children and adolescents during the COVID-19 pandemic: A bibliometric and visualization analysis
-
- Journal:
- Cambridge Prisms: Global Mental Health / Volume 10 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 November 2023, e84
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Anatomical studies and early results on endoscopic transoral medial pterygomandibular fold approach to salvage retropharyngeal lymphadenectomy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 138 / Issue 5 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 November 2023, pp. 540-547
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Whose open science are we talking about? From open science in psychology to open science in applied linguistics
-
- Journal:
- Language Teaching / Volume 56 / Issue 4 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 July 2023, pp. 443-450
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Association study of urinary iodine concentrations and coronary artery disease among adults in the USA: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2003–2018
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 130 / Issue 12 / 28 December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 July 2023, pp. 2114-2122
- Print publication:
- 28 December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Investigation on the opposing jet penetration mode transition mechanism in the hypersonic flow
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 127 / Issue 1317 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 June 2023, pp. 2047-2065
-
- Article
- Export citation
Timing fluctuation correction for the front end of a 100-PW laser
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 June 2023, e52
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Literature review on maritime cybersecurity: state-of-the-art
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Navigation / Volume 76 / Issue 4-5 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 June 2023, pp. 453-466
- Print publication:
- July 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
The study of bioavailability and endogenous circadian rhythm of menaquinone-7, a form of vitamin K2, in healthy subjects
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 130 / Issue 11 / 14 December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 May 2023, pp. 1885-1897
- Print publication:
- 14 December 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation