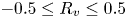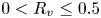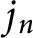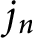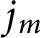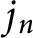103 results
Impact of total parenteral nutrition versus exclusive enteral nutrition on postoperative adverse outcomes in patients with penetrating Crohn’s disease undergoing surgical resection: A retrospective cohort study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 June 2024, pp. 1-28
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Effect of dietary selenium intake on CVD: a retrospective cohort study based on China Health and Nutrition Survey (CHNS) data
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 27 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2024, e122
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
9 - The ‘Effect Doctrine’ and the Extraterritorial Application of Chinese National Laws
- from Part III - Selected Areas of Chinese State Practice
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of China and International Law
- Published online:
- 04 January 2024
- Print publication:
- 18 January 2024, pp 181-200
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Characterization of Energetic Protons Generated in the ShenGuang-II UP Petawatt Laser Interactions with Foil Targets
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2021 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Hydrothermal Experiments Reveal the Influence of Organic Matter on Smectite Illitization
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 66 / Issue 1 / February 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 28-42
-
- Article
- Export citation
Vortex ring formation process in starting jets with uniform background co- and counter-flow
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 968 / 10 August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 August 2023, A26
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Parkes Pulsar Timing Array third data release
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, e049
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Accelerated protons with energies up to 70 MeV based on the optimized SG-II Peta-watt laser facility
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 June 2023, e63
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Drag model of finite-sized particle in turbulent wall-bound flow over sediment bed
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 964 / 10 June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 June 2023, A9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
AI-Based Adherence Prediction for Patients: Leveraging a Mobile Application to Improve Clinical Trials
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 28 / Issue 2 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 April 2023, p. 224
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The intervention effect of humanistic ideological and political management on ruminant thinking of college students and on depression and anxiety
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 March 2023, pp. S25-S26
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Characteristics of patients with SARS-COV-2 PCR re-positivity after recovering from COVID-19
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2023, e34
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A novel multi-shot target platform for laser-driven laboratory astrophysics experiments
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 February 2023, e17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Better is worse, worse is better: Reexamination of violations of dominance in intertemporal choice
-
- Journal:
- Judgment and Decision Making / Volume 12 / Issue 3 / May 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2023, pp. 253-259
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The formation process of annular starting jets
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 949 / 25 October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 October 2022, A47
-
- Article
- Export citation
The global disease burden attributable to a diet low in fibre in 204 countries and territories from 1990 to 2019
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 26 / Issue 4 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 September 2022, pp. 854-865
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Cancer mutation profiles predict ICIs efficacy in patients with non-small cell lung cancer
-
- Journal:
- Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine / Volume 24 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 April 2022, e16
-
- Article
- Export citation
Stieltjes interlacing of the zeros of
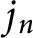 $j_n$
$j_n$
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 65 / Issue 4 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 January 2022, pp. 976-993
- Print publication:
- December 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Relapse risk revealed by degree centrality and cluster analysis in heroin addicts undergoing methadone maintenance treatment
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 6 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2021, pp. 2216-2228
-
- Article
- Export citation