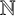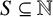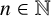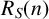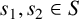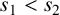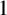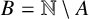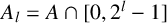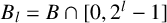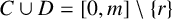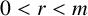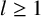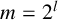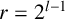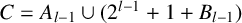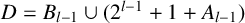165 results
Voltage-gated sodium channel gene mutation and P450 gene expression are associated with the resistance of Aphis spiraecola Patch (Hemiptera: Aphididae) to lambda-cyhalothrin
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 114 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2024, pp. 49-56
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dispersion and Swellability of Ternary Surfactant Co-Modified Montmorillonites
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 69 / Issue 6 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 759-771
-
- Article
- Export citation
Prospect of ultrahigh-resolution fast neutron absorption spectroscopy based on a laser plasma electron accelerator
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 12 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 November 2023, e11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Pulse repetition-rate effect on the intensity inside a femtosecond laser filament in air
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 March 2023, e46
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
FTO: a critical role in obesity and obesity-related diseases
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 130 / Issue 10 / 28 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 March 2023, pp. 1657-1664
- Print publication:
- 28 November 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Added sugar intake and its forms and sources in relation to risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: results from the Tianjin Chronic Low-grade Systemic Inflammation and Health cohort study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 129 / Issue 12 / 28 June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 September 2022, pp. 2094-2101
- Print publication:
- 28 June 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The global disease burden attributable to a diet low in fibre in 204 countries and territories from 1990 to 2019
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 26 / Issue 4 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 September 2022, pp. 854-865
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Late Palaeozoic tectonic evolution of the eastern Palaeo-Asian Ocean: new evidence from the early Permian arc magmatic suites in the Kulun region
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 159 / Issue 9 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 July 2022, pp. 1513-1528
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Early Cretaceous tectonic evolution of the Neo-Tethys: constraints from zircon U–Pb geochronology and geochemistry of the Liuqiong adakite, Gongga, Tibet
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 159 / Issue 10 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 June 2022, pp. 1647-1662
-
- Article
- Export citation
Multiple molecular characteristics of circulating enterovirus types among paediatric hand, foot and mouth disease patients after EV71 vaccination campaign in Wuxi, China
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 April 2022, e98
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Maternal diet quality during pregnancy and its influence on low birth weight and small for gestational age: a birth cohort in Beijing, China
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 129 / Issue 8 / 28 April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 March 2022, pp. 1360-1369
- Print publication:
- 28 April 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
ON INTEGER SETS WITH THE SAME REPRESENTATION FUNCTIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 106 / Issue 2 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 March 2022, pp. 224-235
- Print publication:
- October 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Organ meat consumption and risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: the Tianjin Chronic Low-grade Systemic Inflammation and Health cohort study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 130 / Issue 2 / 28 July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2022, pp. 276-283
- Print publication:
- 28 July 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
The clinical and neuroimaging features of sporadic adult-onset neuronal intranuclear inclusion disease
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 50 / Issue 2 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 February 2022, pp. 243-248
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Cladding-pumped Raman fiber laser with 0.78% quantum defect enabled by phosphorus-doped fiber
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 10 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 January 2022, e8
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Schistosomiasis in the People's Republic of China – down but not out
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 149 / Issue 2 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 November 2021, pp. 218-233
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
2-kW-level superfluorescent fiber source with flexible wavelength and linewidth tunable characteristics
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 9 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 October 2021, e55
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effects of dietary tryptophan on muscle growth, protein synthesis and antioxidant capacity in hybrid catfish Pelteobagrus vachelli♀ × Leiocassis longirostris♂
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 127 / Issue 12 / 28 June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 July 2021, pp. 1761-1773
- Print publication:
- 28 June 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The population characteristics of the main leukocyte subsets and their association with chronic diseases in a community-dwelling population: a cross-sectional study
-
- Journal:
- Primary Health Care Research & Development / Volume 22 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 May 2021, e18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation