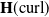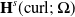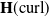131 results
Multiple model fault diagnosis and fault tolerant control for the launch vehicle’s attitude control system
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 May 2024, pp. 1-20
-
- Article
- Export citation
Trauma diagnostic-related target proteins and their detection techniques
-
- Journal:
- Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine / Volume 26 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2024, e7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Advanced Glycation End Products’ Receptor DNA Methylation Associated with Immune Infiltration and Prognosis of Lung Adenocarcinoma and Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Horizontal FDI and Internal R&D of Local Firms in Emerging Economies: A Coopetition Perspective
-
- Journal:
- Management and Organization Review / Volume 19 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2023, pp. 981-1004
-
- Article
- Export citation
Linear global stability of a flow past a sphere under a streamwise magnetic field
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 970 / 10 September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 August 2023, A16
-
- Article
- Export citation
Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway in breast cancer cells and its effect on reversing tumour drug resistance by alkaloids extracted from traditional Chinese medicine
-
- Journal:
- Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine / Volume 25 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 June 2023, e21
-
- Article
- Export citation
Molecular cytology identification of 22 sugarcane germplasm clones from Sri Lanka
-
- Journal:
- Plant Genetic Resources / Volume 20 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 May 2023, pp. 377-382
-
- Article
- Export citation
Factual and counterfactual learning in major adolescent depressive disorder, evidence from an instrumental learning study
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 2 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 May 2023, pp. 256-266
-
- Article
- Export citation
Prehospital Nursing Volunteer’s Personality Traits: A Motivational Perspective
-
- Journal:
- Prehospital and Disaster Medicine / Volume 38 / Issue S1 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 July 2023, p. s162
- Print publication:
- May 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Food Sources May Affect the Symptom Rates of COVID-19, an Epidemiological Analysis Based on the Public Data in Gansu Province, China, During the Summer Epidemic Cycle in 2022
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 17 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2023, e393
-
- Article
- Export citation
Growth, development, and host preference of Histiostoma feroniarum (Acaridida: Histiostomatidae): effects of temperature and types of mushroom cultivar
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 113 / Issue 3 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 March 2023, pp. 412-418
-
- Article
- Export citation
High-energy, hundred-picosecond pulsed 266 nm mid-ultraviolet generation by a barium borate crystal
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 March 2023, e31
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Solving two-dimensional H(curl)-elliptic interface systems with optimal convergence on unfitted meshes
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics / Volume 34 / Issue 4 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2023, pp. 774-805
-
- Article
- Export citation
The global disease burden attributable to a diet low in fibre in 204 countries and territories from 1990 to 2019
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 26 / Issue 4 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 September 2022, pp. 854-865
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Risk factors for underlying comorbidities and complications in patients with hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2022, e147
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Understanding children’s perspectives of the influences on their dietary behaviours
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 25 / Issue 8 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 February 2022, pp. 2156-2166
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Consistent brain structural abnormalities and multisite individualised classification of schizophrenia using deep neural networks
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 221 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 February 2022, pp. 732-739
- Print publication:
- December 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Schistosomiasis in the People's Republic of China – down but not out
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 149 / Issue 2 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 November 2021, pp. 218-233
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
A Comparison of Preterm Birth Rate and Growth from Birth to 18 Years Old between in Vitro Fertilization and Spontaneous Conception of Twins
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 24 / Issue 4 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2021, pp. 228-233
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effects of dietary tryptophan on muscle growth, protein synthesis and antioxidant capacity in hybrid catfish Pelteobagrus vachelli♀ × Leiocassis longirostris♂
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 127 / Issue 12 / 28 June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 July 2021, pp. 1761-1773
- Print publication:
- 28 June 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation