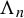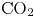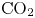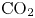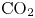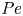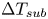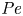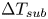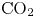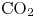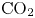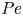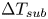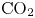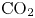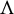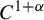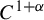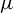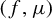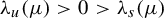124 results
Pore-scale study of CO2 desublimation and sublimation in a packed bed during cryogenic carbon capture
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 990 / 10 July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 August 2024, A6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Primary plastic polymers: Urgently needed upstream reduction
-
- Journal:
- Cambridge Prisms: Plastics / Volume 2 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 April 2024, e7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A set-theoretic approach to algebraic L-domains
-
- Journal:
- Mathematical Structures in Computer Science / Volume 34 / Issue 3 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2024, pp. 244-257
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Relationship between syncopal symptoms and head-up tilt test modes
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 April 2024, pp. 1-6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dimension estimates and approximation in non-uniformly hyperbolic systems
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 February 2024, pp. 1-27
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Inverse association between maternal serum concentrations of trace elements and risk of spontaneous preterm birth: a nested case–control study in China
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 8 / 28 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2024, pp. 1425-1435
- Print publication:
- 28 April 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Identification of Important Genes of Keratoconus and Construction of the Diagnostic Model
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e31
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Downregulated miR-150-5p in the Tissue of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e34
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Identification of Key Biomarkers and Candidate Molecules in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer by Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e29
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The origins of saddles and riding technology in East Asia: discoveries from the Mongolian Altai
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Composition and diversity of the gut microbiota across different life stages of American cockroach (Periplaneta americana)
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 113 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 December 2023, pp. 787-793
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Integrated safety analysis of phase 3 studies for investigational microbiome therapeutic, SER-109, in recurrent CDI
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, pp. s44-s45
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Adolescent psychological adjustment and social supports during pandemic-onset remote learning: A national multi-wave daily-diary study
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology / Volume 35 / Issue 5 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 September 2023, pp. 2533-2550
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
RNA N6-methyladenosine of DHAPAT and PAP involves in regulation of diapause of Bombyx mori via the lipid metabolism pathway
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 113 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 August 2023, pp. 665-675
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Neural habituation during acute stress signals a blunted endocrine response and poor resilience
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 16 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 June 2023, pp. 7735-7745
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Study of CO2 desublimation during cryogenic carbon capture using the lattice Boltzmann method
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 964 / 10 June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 May 2023, A1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dimension approximation in smooth dynamical systems
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems / Volume 44 / Issue 2 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2023, pp. 383-407
- Print publication:
- February 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Pulse repetition-rate effect on the intensity inside a femtosecond laser filament in air
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 March 2023, e46
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Categorizing People in the New States: A Comparative Study of Communist China and North Korea
-
- Journal:
- Journal of East Asian Studies / Volume 23 / Issue 2 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 March 2023, pp. 185-203
- Print publication:
- July 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation