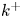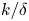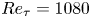125 results
The effect of the universal two-child policy on the gender wage gap in urban China
-
- Journal:
- The Economic and Labour Relations Review ,
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 September 2024, pp. 1-20
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Childhood socio-economic disadvantages versus adverse care experiences: Mediation and moderation impacts on late-life depressive symptoms
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 67 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 August 2024, e47
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Phylogenetic trends in TZ staining analysis of six deep dormancy seeds
-
- Journal:
- Seed Science Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2024, pp. 1-13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Transition in metabolic health phenotypes across general adiposity categories and association with the risk of depression: a prospective analysis
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 67 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 February 2024, e26
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Experimental electron density distribution of KZnB3O6 constructed by maximum-entropy method
-
- Journal:
- Powder Diffraction / Volume 38 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 February 2024, pp. 233-239
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Cisuralian–Guadalupian brachiopod assemblages from the northern Tengchong Block in western Yunnan, China and their paleogeographical implications—a revisit
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Paleontology / Volume 98 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 February 2024, pp. 47-78
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
China’s prevention and control experience of echinococcosis: A 19-year retrospective
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 98 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2024, e16
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
An Integrative Multi-Omics Analysis Based on Nomogram for Predicting Prostate Cancer Bone Metastasis Incidence
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A Cell Differentiation Trajectory-Related Signature for Predicting the Prognosis of Lung Adenocarcinoma
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e42
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The association between childhood maltreatment and internet addiction among Chinese junior middle school students: prospective cohort study
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 10 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 December 2023, e5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Association between the dietary antioxidant index and relative telomere length of leucocytes in the Chinese population
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 6 / 28 March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2023, pp. 1031-1040
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Supersonic gas jet stabilization in laser–plasma acceleration
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 October 2023, e91
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Outer-layer similarity and energy transfer in a rough-wall turbulent channel flow
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 968 / 10 August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 August 2023, A18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Factual and counterfactual learning in major adolescent depressive disorder, evidence from an instrumental learning study
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 2 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 May 2023, pp. 256-266
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Persistent eutrophication and hypoxia in the coastal ocean
-
- Journal:
- Cambridge Prisms: Coastal Futures / Volume 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 February 2023, e19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The effect of the universal two-child policy on female labour market outcomes in China
-
- Journal:
- The Economic and Labour Relations Review / Volume 33 / Issue 3 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2023, pp. 526-546
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The more the better? How and when can high-performance work systems fuel the proactive fire
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Management & Organization , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2022, pp. 1-18
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Actual Status of Hospitals as COVID-19 Vaccination Clinics in China and Safety Monitoring of Inactivated Vaccine: A Cross-Sectional Study
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 17 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 August 2022, e256
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A self-biased GaN LNA with 30 dB gain and 21 dBm P1dB for 5G communications
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies / Volume 15 / Issue 4 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 August 2022, pp. 547-553
-
- Article
- Export citation
Structural Analysis for Highly Aligned Graphene Fold on Cu(111) Substrate
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2022, pp. 2512-2514
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation