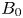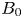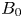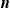210 results
Non-universality and dissipative anomaly in compressible magnetohydrodynamic turbulence
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 992 / 10 August 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 August 2024, A9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Three-dimensional path planning with enhanced gravitational search algorithm for unmanned aerial vehicle
-
- Journal:
- Robotica , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 May 2024, pp. 1-35
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Global, regional and national burdens of depression in adolescents and young adults aged 10–24 years, from 1990 to 2019: findings from the 2019 Global Burden of Disease study
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry , FirstView
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 April 2024, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Strategic underreporting and optimal deductible insurance
-
- Journal:
- ASTIN Bulletin: The Journal of the IAA , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, pp. 1-24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Quantifying stakeholders’ preference for implantable medical devices in China: a discrete choice experiment
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care / Volume 40 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2024, e8
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Compact Thomson Scattering Source Based on a Mixed Injection Assisted Laser Wakefield Accelerator
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Genetic Analysis of Prunus salicina L. by Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA (RAPD) and Intersimple Sequence Repeat (ISSR)
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e63
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Energy transfer and third-order law in forced anisotropic magneto-hydrodynamic turbulence with hyper-viscosity
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 974 / 10 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, A20
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Relationship between homocysteine and chronic total coronary occlusion: a cross-sectional study from southwest China
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 34 / Issue 4 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 October 2023, pp. 740-747
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Generalised solution to a 2D parabolic-parabolic chemotaxis system for urban crime: Global existence and large-time behaviour
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics / Volume 35 / Issue 3 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 September 2023, pp. 409-429
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Reinsurance games with
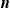 $\boldsymbol{{n}}$ variance-premium reinsurers: from tree to chain
$\boldsymbol{{n}}$ variance-premium reinsurers: from tree to chain
-
- Journal:
- ASTIN Bulletin: The Journal of the IAA / Volume 53 / Issue 3 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 July 2023, pp. 706-728
- Print publication:
- September 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Granitic magmatism associated with gold mineralization: evidence from the Baizhangzi gold deposit, in the northern North China Craton
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 160 / Issue 6 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 June 2023, pp. 1211-1227
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Experimental synthesis and crystal structure refinement of a new ternary intermetallic compound Al3GaCu9
-
- Journal:
- Powder Diffraction / Volume 38 / Issue 3 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 May 2023, pp. 215-219
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The complete mitochondrial genome of Ogmocotyle ailuri: gene content, composition and rearrangement and phylogenetic implications
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 150 / Issue 8 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 April 2023, pp. 661-671
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Pulse repetition-rate effect on the intensity inside a femtosecond laser filament in air
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 March 2023, e46
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Late Permian to early Triassic gabbro in North Lhasa, Tibet: evidence for plume - subduction-zone interaction of the Palaeo-Tethys ocean – RETRACTION
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 160 / Issue 2 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 March 2023, p. 409
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Development of EST-SSR markers for an endangered plant species, Camellia fascicularis (Theaceae)
-
- Journal:
- Plant Genetic Resources / Volume 20 / Issue 4 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 March 2023, pp. 263-269
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Tunable compact asynchronous optical sampling system using Er-doped fiber laser
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 March 2023, e29
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation