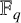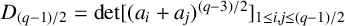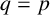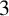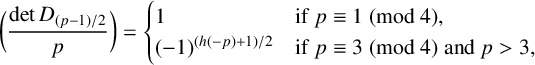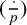807 results

Australian Banking and Finance Law and Regulation
- Coming soon
-
- Expected online publication date:
- July 2024
- Print publication:
- 31 July 2024
-
- Textbook
- Export citation
Choosing innovation alliance governance structure: The roles of performance feedback and top management team characteristics
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Management & Organization , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 June 2024, pp. 1-23
-
- Article
- Export citation
Resistance patterns and molecular basis to ACCase-inhibiting herbicides
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science , FirstView
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 May 2024, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
- Export citation
Comparison of ten policy options to equitably reduce children’s exposure to unhealthy food marketing
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 27 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 April 2024, e130
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
ON GENERALISED LEGENDRE MATRICES INVOLVING ROOTS OF UNITY OVER FINITE FIELDS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 April 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
- Export citation
Macrolide resistance of Mycoplasma pneumoniae in several regions of China from 2013 to 2019
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, e75
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Multidimensional credibility: A new approach based on joint distribution function
-
- Journal:
- ASTIN Bulletin: The Journal of the IAA , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 April 2024, pp. 1-27
-
- Article
- Export citation
Psychosocial and psychological interventions for schizophrenia relapse prevention: A bibliometric analysis
-
- Journal:
- Cambridge Prisms: Global Mental Health / Volume 11 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 April 2024, e49
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Super-efficient Reduction of 4-nitrophenol Using Raw Pelagic Clays as Catalysts
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 71 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, pp. 745-759
-
- Article
- Export citation
On optimal reinsurance in the presence of premium budget constraint and reinsurer’s risk limit
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 March 2024, pp. 1-28
-
- Article
- Export citation
Alexithymia and peer victimisation: interconnected pathways to adolescent non-suicidal self-injury – ERRATUM
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 10 / Issue 2 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 March 2024, e65
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Temporal changes in brain morphology related to inflammation and schizophrenia: an omnigenic Mendelian randomization study
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 March 2024, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Models of mild cognitive deficits in risk assessment in early psychosis
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 March 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
- Export citation
The role of the peer effect in forming pension expectations among the middle-aged: existence and mechanisms
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Pension Economics & Finance , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 February 2024, pp. 1-25
-
- Article
- Export citation
Chinese stalagmite δ18O records reveal the diverse moisture trajectories during the middle to late last glacial period
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 February 2024, pp. 1-13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Alexithymia and peer victimisation: interconnected pathways to adolescent non-suicidal self-injury
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 10 / Issue 2 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 February 2024, e46
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A continuous-wave Nd:YVO4-KGW intracavity Raman laser with over 34% diode-to-Stokes optical efficiency
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 12 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 February 2024, e19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Inverse association between maternal serum concentrations of trace elements and risk of spontaneous preterm birth: a nested case–control study in China
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 8 / 28 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2024, pp. 1425-1435
- Print publication:
- 28 April 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Plasma Spectroscopy on Hydrogen-Carbon-Oxygen Foam Targets Driven by Laser-Generated Hohlraum Radiation
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation