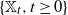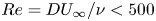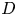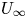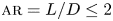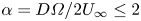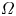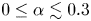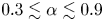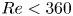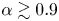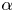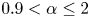155 results
Seasonality in regional brain glucose metabolism
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effectiveness of a WHO self-help psychological intervention to alleviate stress among healthcare workers in the context of COVID-19 in China: a randomised controlled trial
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 33 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 March 2024, e11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effect of vegetable consumption on risk of gastric cancer: a systematic review and multi-level meta-analysis of prospective studies
-
- Journal:
- Nutrition Research Reviews , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 February 2024, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
- Export citation
Adsorption of atrazine and paraquat on montmorillonite loaded with layered double hydroxide and active site energy distribution analysis
-
- Journal:
- Clay Minerals , FirstView
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 February 2024, pp. 1-13
-
- Article
- Export citation
Cavitation bubble dynamics inside a droplet suspended in a different host fluid
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 979 / 25 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 January 2024, A47
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Construction and Characterization of a Nanostructured Biocatalyst Consisting of Immobilized Lipase on Mg-Amino-Clay
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 69 / Issue 4 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 434-442
-
- Article
- Export citation
Plasma Spectroscopy on Hydrogen-Carbon-Oxygen Foam Targets Driven by Laser-Generated Hohlraum Radiation
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Cross-Section Measurements of the 11B(p,α)2α Reaction near the First Resonant Energy
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Association between the PLTP rs4810479 SNP and Serum Lipid Traits in the Chinese Maonan and Han Populations
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2021 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e14
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dispersion and Swellability of Ternary Surfactant Co-Modified Montmorillonites
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 69 / Issue 6 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 759-771
-
- Article
- Export citation
Enhancement of Magnetic Vortex Acceleration by Laser Interaction with Near-Critical Density Plasma inside a Hollow Conical Target
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Associations between Extracellular Matrix Protein 1 Gene Polymorphism and Progression of Liver Disease
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e21
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Energy Dependency of Proton-Induced Outer-Shell Multiple Ionization for 48Cd and 49In
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2021 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e22
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Overexpressed Histocompatibility Minor 13 was Associated with Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression and Prognosis
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e23
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Reevaluation of the protein requirement in Chinese elderly adults without sarcopenia with the indicator amino acid oxidation technique
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 8 / 28 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 December 2023, pp. 1377-1383
- Print publication:
- 28 April 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Weak convergence of the extremes of branching Lévy processes with regularly varying tails
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 December 2023, pp. 1-22
-
- Article
- Export citation
Digital generation of super-Gaussian perfect vortex beams via wavefront shaping with globally adaptive feedback
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 12 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 November 2023, e5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Numerical analyses of the flow past a short rotating cylinder
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 975 / 25 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 November 2023, A15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation