127 results
Comparisons between dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry and bioimpedance devices for appendicular lean mass and muscle quality in Hispanic adults
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 12 / 28 June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2024, pp. 2031-2038
- Print publication:
- 28 June 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Random pinhole attenuator for high-power laser beams
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 April 2024, pp. 1-17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
P86: Effect of Virtual Reality on Stress Reduction and Change of Physiological Parameters Including Heart Rate Variability in People With High Stress: An Open Randomized Crossover Trial
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 35 / Issue S1 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2024, pp. 129-130
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
PP50 Early Diagnosis Effect Of Newborns With Critical Congenital Heart Disease Using National Health Insurance Data In South Korea
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care / Volume 39 / Issue S1 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 December 2023, p. S66
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
PP122 The Feasibility Assessment For Domestic Introduction Of Newborn Pulse Oximetry Screening For Critical Congenital Heart Disease
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care / Volume 39 / Issue S1 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 December 2023, p. S84
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Comparison of Perceived Importance and Performance of Community Pharmacists’ Role in South Korea During the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 17 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 December 2023, e569
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Application of Deep Learning to Solar and Space Weather Data
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 18 / Issue S372 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 September 2023, pp. 131-149
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Outbreak of COVID-19 among children and young adults in a cancer centre daycare unit
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 February 2022, e40
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on depression in community-dwelling older adults: a prospective cohort study
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 7 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 December 2021, pp. 2992-2999
-
- Article
- Export citation
Impact of data extraction errors in meta-analyses on the association between depression and peripheral inflammatory biomarkers: an umbrella review
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 5 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 November 2021, pp. 2017-2030
-
- Article
- Export citation
Manufacturers’ perceptions of the decision-making process for new drug reimbursement in South Korea
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care / Volume 37 / Issue 1 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 September 2021, e88
-
- Article
- Export citation
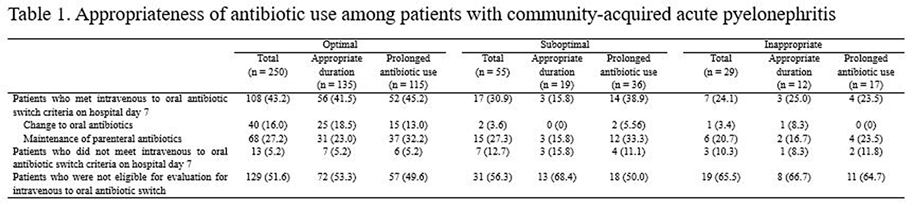
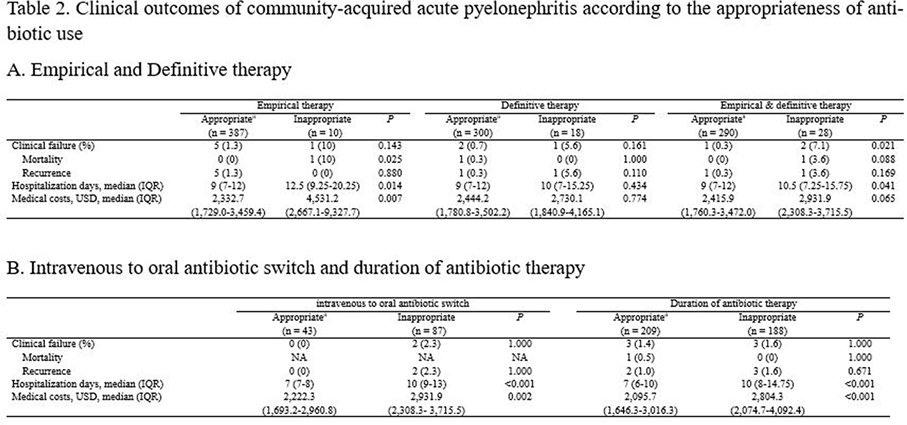
Differences in the Clinical Outcome of Community-Acquired APN According to the Appropriateness of Antibiotic Use
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 1 / Issue S1 / July 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 July 2021, p. s6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Clinical impact of early reinsertion of a central venous catheter after catheter removal in patients with catheter-related bloodstream infections
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 42 / Issue 2 / February 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 September 2020, pp. 162-168
- Print publication:
- February 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Imperatives of Care: Women and Medicine in Colonial Korea. By Sonja M. Kim. Honolulu: University of Hawai‘i Press, 2019. 232 pp. ISBN: 9780824855451 (cloth).
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Asian Studies / Volume 79 / Issue 3 / August 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 October 2020, pp. 780-781
- Print publication:
- August 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Whole-genome sequencing combined with a case-control study of an outbreak of staphylococcal food-poisoning
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 May 2020, pp. 1-16
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The Differential Cognitive Deficits Between Patients with Early Stage Alzheimer's Disease and Patients with Early Stage Vascular Dementia
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 41 / Issue S1 / April 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 March 2020, p. S175
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Preserved Serotonergic Activity in Early-Onset Parkinson’s Disease
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 47 / Issue 3 / May 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 November 2019, pp. 344-349
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effects of a Korean version of the metacognitive training program for outpatients with schizophrenia on theory of mind, positive symptoms, and interpersonal relationships
-
- Journal:
- Behavioural and Cognitive Psychotherapy / Volume 48 / Issue 1 / January 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 October 2019, pp. 14-24
- Print publication:
- January 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Alexithymia and frontal–amygdala functional connectivity in North Korean refugees
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 50 / Issue 2 / January 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 February 2019, pp. 334-341
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Looking backward through the looking glass: Reference groups and social comparison
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Management & Organization / Volume 26 / Issue 1 / January 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 November 2018, pp. 110-131
-
- Article
- Export citation