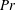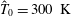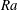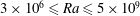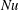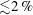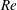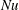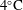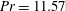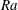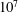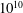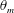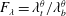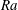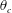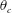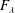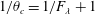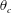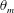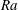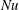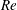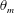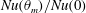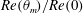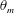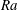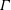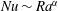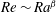19 results
Voltage-gated sodium channel gene mutation and P450 gene expression are associated with the resistance of Aphis spiraecola Patch (Hemiptera: Aphididae) to lambda-cyhalothrin
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 114 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2024, pp. 49-56
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dispersion and Swellability of Ternary Surfactant Co-Modified Montmorillonites
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 69 / Issue 6 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 759-771
-
- Article
- Export citation
Prevalence of invasive aspergillosis in suspected pulmonary tuberculosis at a referral tuberculosis hospital in Shandong, China
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 148 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 November 2020, e275
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
CURB-65 may serve as a useful prognostic marker in COVID-19 patients within Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 148 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 October 2020, e241
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Trends of the incidence of drug use disorders from 1990 to 2017: an analysis based on the Global Burden of Disease 2017 data
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 29 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 August 2020, e148
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
On non-Oberbeck–Boussinesq effects in Rayleigh–Bénard convection of air for large temperature differences
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 889 / 25 April 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 February 2020, A10
-
- Article
- Export citation
Serum folate concentrations at diagnosis are associated with hepatocellular carcinoma survival in the Guangdong Liver Cancer Cohort study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 121 / Issue 12 / 28 June 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 June 2019, pp. 1376-1388
- Print publication:
- 28 June 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Penetrative turbulent Rayleigh–Bénard convection in two and three dimensions
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 870 / 10 July 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 May 2019, pp. 718-734
-
- Article
- Export citation
A prospective observation on nutrition support in adult patients with severe burns
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 121 / Issue 9 / 14 May 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 February 2019, pp. 974-981
- Print publication:
- 14 May 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The study on the early warning period of varicella outbreaks based on logistic differential equation model
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 147 / 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2019, e70
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Laboratory study of astrophysical collisionless shock at SG-II laser facility
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 6 / 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 September 2018, e45
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Flow reversals in two-dimensional thermal convection in tilted cells
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 849 / 25 August 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 June 2018, pp. 355-372
-
- Article
- Export citation
Quantification of Electron Beam Heating Effect in TEM
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 23 / Issue S1 / July 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 August 2017, pp. 1766-1767
- Print publication:
- July 2017
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
In-situThermal Testing on Nanostructures in TEM
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 22 / Issue S3 / July 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 July 2016, pp. 770-771
- Print publication:
- July 2016
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Utilizing the Resource of Twins Reared Apart: Their Distribution Across Nine Provinces or Cities of China
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 18 / Issue 2 / April 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 March 2015, pp. 210-216
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Review of the current status of fast ignition research at the IAPCM
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 2 / 01 July 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 March 2014, e6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A joint diagnostic system for laser-driven shock wave experiments
-
- Journal:
- The European Physical Journal - Applied Physics / Volume 62 / Issue 3 / June 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 June 2013, 31001
- Print publication:
- June 2013
-
- Article
- Export citation
Properties of Au/Pb(Zr0.52Ti0.48)O3/ Bi4Ti3O12/p-Si Ferroelectric Memory Diodes
-
- Journal:
- MRS Online Proceedings Library Archive / Volume 655 / 2000
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 March 2011, CC5.1.1
- Print publication:
- 2000
-
- Article
- Export citation
Epitaxial Growth of CoSi2/Si Hetero-Structure by Solid State Interaction of Co/Ti/Si Multilayer
-
- Journal:
- MRS Online Proceedings Library Archive / Volume 337 / 1994
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 February 2011, 449
- Print publication:
- 1994
-
- Article
- Export citation