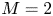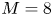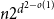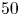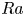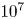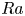397 results
Inverse association between maternal serum concentrations of trace elements and risk of spontaneous preterm birth: a nested case–control study in China
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 8 / 28 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2024, pp. 1425-1435
- Print publication:
- 28 April 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Detecting Chlorite in the Chinese Loess Sequence by Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 54 / Issue 2 / April 2006
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 266-273
-
- Article
- Export citation
Preparation and Characterization of Halloysite-Based Carriers for Quercetin Loading and Release
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 69 / Issue 1 / February 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 94-104
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dispersion and Swellability of Ternary Surfactant Co-Modified Montmorillonites
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 69 / Issue 6 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 759-771
-
- Article
- Export citation
Rapid and Quantitative Measurement of Hematite and Goethite in the Chinese Loess-Paleosol Sequence by Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 50 / Issue 2 / April 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 208-216
-
- Article
- Export citation
Artificial Selection Drives SNPs of Olfactory Receptor Genes into Different Working Traits in Labrador Retrievers
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e77
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Properties of Clay Minerals in Soil Particles from Two Ultisols, China
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 65 / Issue 4 / August 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 273-285
-
- Article
- Export citation
Association Between Dysmenorrhea and Risk of Epilepsy in East Asian Populations: A Bidirectional Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 26 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 December 2023, pp. 361-369
-
- Article
- Export citation
Comprehensive Multiomics Analysis of Monozygotic Twin Discordant for Double Outlet Right Ventricle
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 26 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 December 2023, pp. 370-378
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Digital generation of super-Gaussian perfect vortex beams via wavefront shaping with globally adaptive feedback
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 12 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 November 2023, e5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Conditional analysis on extreme wall shear stress and heat flux events in compressible turbulent boundary layers
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 974 / 10 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 November 2023, A38
-
- Article
- Export citation
Many Hamiltonian subsets in large graphs with given density
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 33 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 October 2023, pp. 110-120
-
- Article
- Export citation
Genetic and Environmental Influences on Blood Pressure and Serum Lipids Across Age-Groups
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 26 / Issue 3 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 August 2023, pp. 223-230
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effect of subsurface impurity defects on laser damage resistance of beam splitter coatings
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 May 2023, e61
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
On the thermal effect of porous material in porous media Rayleigh–Bénard convection
-
- Journal:
- Flow: Applications of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 3 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 May 2023, E13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Molecular cytology identification of 22 sugarcane germplasm clones from Sri Lanka
-
- Journal:
- Plant Genetic Resources / Volume 20 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 May 2023, pp. 377-382
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Welfare Cost of Beijing’s Lottery Policy: Evidence from a Contingent Valuation Survey
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Benefit-Cost Analysis / Volume 14 / Issue 2 / Summer 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 May 2023, pp. 251-274
-
- Article
- Export citation
Weight self-misperception and obesity-related knowledge, attitudes, lifestyle behaviours and cardio-metabolic markers among Chinese school-aged children and adolescents
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 26 / Issue 8 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 April 2023, pp. 1549-1561
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The complete mitochondrial genome of Ogmocotyle ailuri: gene content, composition and rearrangement and phylogenetic implications
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 150 / Issue 8 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 April 2023, pp. 661-671
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Pulse repetition-rate effect on the intensity inside a femtosecond laser filament in air
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 March 2023, e46
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation