17 results
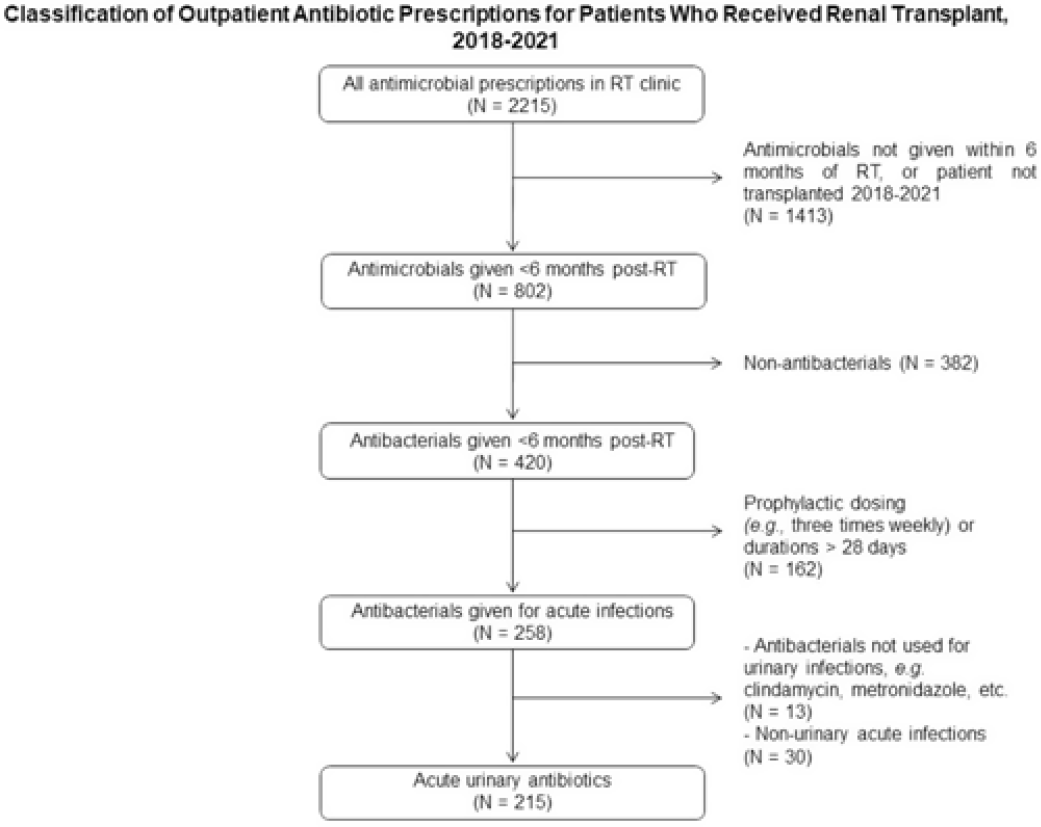
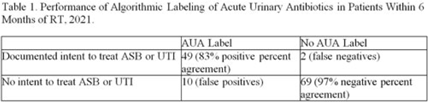
“Acute urinary antibiotics”—A simple metric to identify outpatient antibiotic stewardship opportunities in renal transplant
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, pp. s76-s77
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
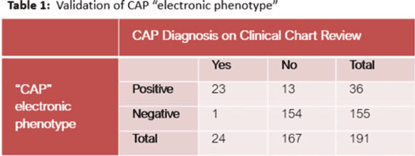
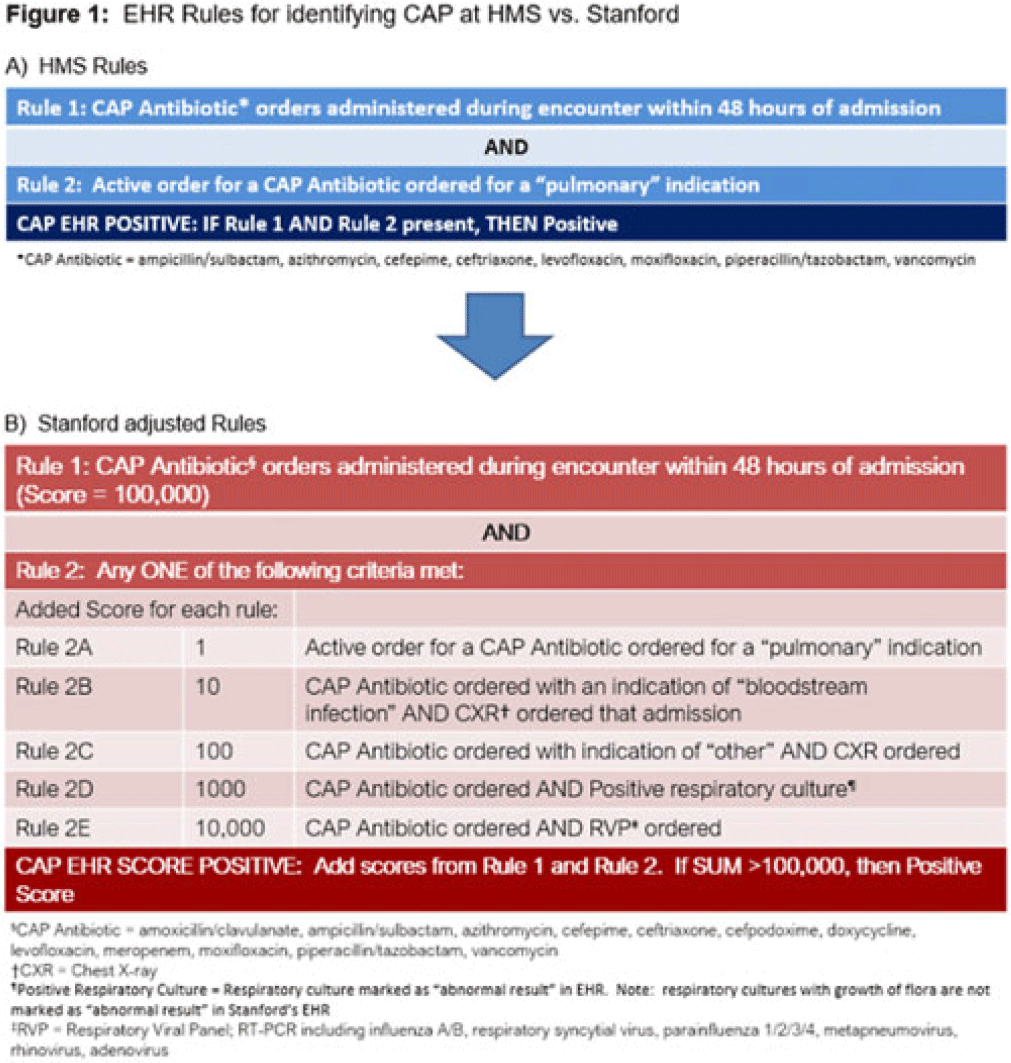
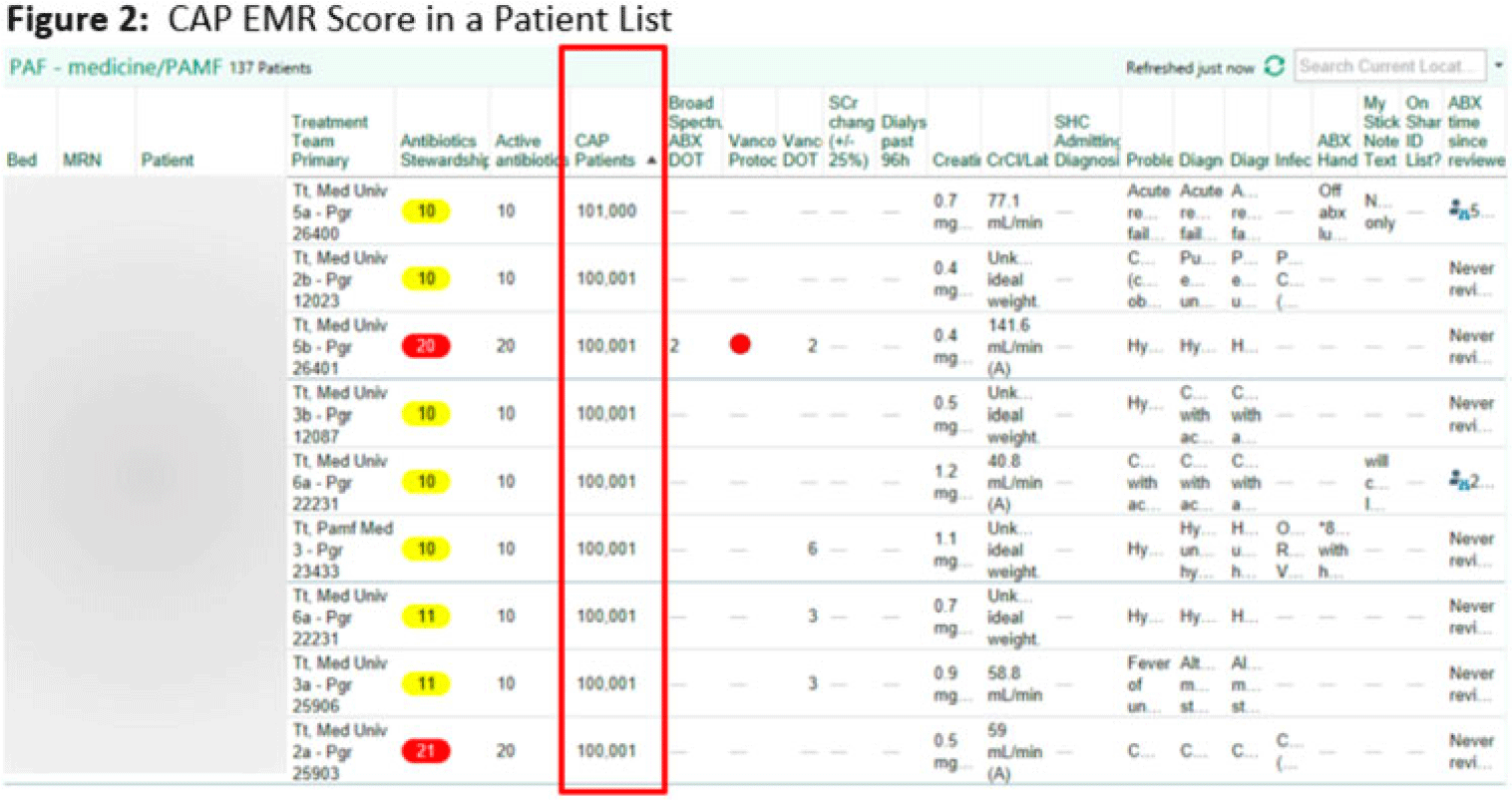
Electronic phenotyping of community-acquired pneumonia: A tool for inpatient syndrome-specific antimicrobial stewardship
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, pp. s114-s115
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
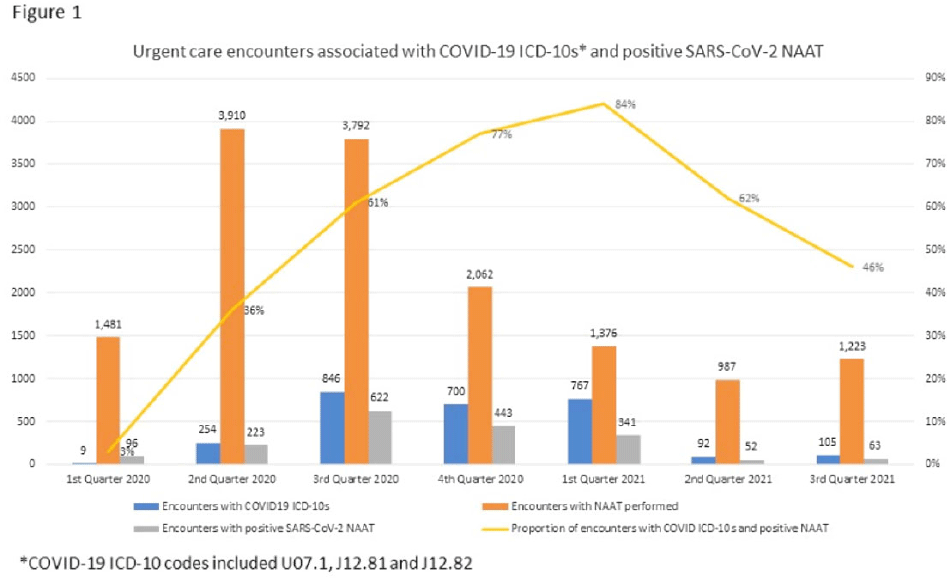
A quality-improvement approach to urgent-care antibiotic stewardship for respiratory tract infections during the COVID-19 pandemic: Lessons learned
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 12 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 February 2023, pp. 2022-2027
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
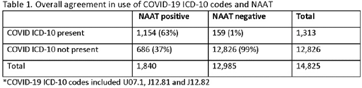
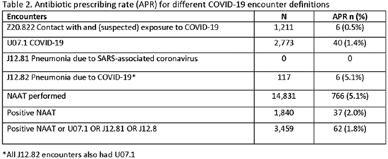
Impact of different COVID-19 encounter definitions on antibiotic prescribing rates in urgent care
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 2 / Issue S1 / July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 May 2022, p. s5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Metrics in outpatient stewardship: Is more always better?
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 2 / Issue S1 / July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 May 2022, pp. s70-s71
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Outpatient hydroxychloroquine prescribing at a large academic health system during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 42 / Issue 3 / March 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 May 2020, pp. 377-378
- Print publication:
- March 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Simulation-based research in emergency medicine in Canada: Priorities and perspectives
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Emergency Medicine / Volume 22 / Issue 1 / January 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 September 2019, pp. 103-111
- Print publication:
- January 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Cryo-EM Structure of Nipah Virus Fusion Glycoprotein in Complex with a Monoclonal Antibody Reveals Mechanism of Neutralization
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 25 / Issue S2 / August 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 August 2019, pp. 1328-1329
- Print publication:
- August 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A Quantitative Evaluation of Microstructure by Electron Back-Scattered Diffraction Pattern Quality Variations
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 19 / Issue S5 / August 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 August 2013, pp. 83-88
- Print publication:
- August 2013
-
- Article
- Export citation
Randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of olanzapine in patients with bipolar I depression
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 201 / Issue 5 / November 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 January 2018, pp. 376-382
- Print publication:
- November 2012
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
‘Catalytic’ doses of fructose may benefit glycaemic control without harming cardiometabolic risk factors: a small meta-analysis of randomised controlled feeding trials
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 108 / Issue 3 / 14 August 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 February 2012, pp. 418-423
- Print publication:
- 14 August 2012
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Contributors
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Dictionary of Christianity
- Published online:
- 05 August 2012
- Print publication:
- 20 September 2010, pp xi-xliv
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Personality and Political Attitudes: Relationships across Issue Domains and Political Contexts
-
- Journal:
- American Political Science Review / Volume 104 / Issue 1 / February 2010
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 March 2010, pp. 111-133
- Print publication:
- February 2010
-
- Article
- Export citation
Molecular Beam Epitaxy Growth of High Mobility Compound Semiconductor Devices for Integration with Si CMOS
-
- Journal:
- MRS Online Proceedings Library Archive / Volume 1194 / 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2011, 1194-A09-01
- Print publication:
- 2009
-
- Article
- Export citation
Electrically Modulated Drug Delivery using Nanoporous Electrodes
-
- Journal:
- MRS Online Proceedings Library Archive / Volume 1239 / 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2011, 1239-VV08-03
- Print publication:
- 2009
-
- Article
- Export citation
Direct Growth of III-V Devices on Silicon
-
- Journal:
- MRS Online Proceedings Library Archive / Volume 1068 / 2008
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 February 2011, 1068-C02-01
- Print publication:
- 2008
-
- Article
- Export citation
behavioral aspects of lesch–nyhan disease and its variants
-
- Journal:
- Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology / Volume 47 / Issue 10 / October 2005
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 September 2005, pp. 673-677
- Print publication:
- October 2005
-
- Article
- Export citation