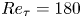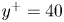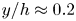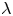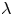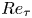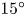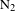32 results
Evaluation of the psychometrics of the Social Impact Scale and its association with depression among asymptomatic COVID-19 carriers
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 10 / Issue 2 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 February 2024, e41
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A resolvent-based prediction framework for incompressible turbulent channel flow with limited measurements
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 976 / 10 December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 December 2023, A31
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Review of Activity Within Unscheduled Care at Royal Cornhill Post-Pandemic
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 9 / Issue S1 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 July 2023, p. S172
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Variation in placental microRNA expression associates with maternal family history of cardiovascular disease
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease / Volume 14 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 July 2022, pp. 132-139
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Evaluation of iodine nutritional status during pregnancy by estimated 24-h urinary iodine excretion: population variation range and individual accuracy
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 25 / Issue 2 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 August 2021, pp. 237-247
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Trends and influencing factors of plasma folate levels in Chinese women at mid-pregnancy, late pregnancy and lactation periods
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 126 / Issue 6 / 28 September 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 December 2020, pp. 885-891
- Print publication:
- 28 September 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Associations of fat and carbohydrate intake with becoming overweight and obese: an 11-year longitudinal cohort study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 124 / Issue 7 / 14 October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 May 2020, pp. 715-728
- Print publication:
- 14 October 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
PP108 Assessing CHA2DS2-VASc Score For Predicting Ischemic Stroke In The Non-Atrial Fibrillation Population
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care / Volume 35 / Issue S1 / 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 December 2019, p. 58
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Impact of calcium, vitamin D, vitamin K, oestrogen, isoflavone and exercise on bone mineral density for osteoporosis prevention in postmenopausal women: a network meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 123 / Issue 1 / 14 January 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 September 2019, pp. 84-103
- Print publication:
- 14 January 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Thymidylate synthase gene variation is associated with the risk for conotruncal heart defects in Chinese population
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 29 / Issue 3 / March 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2018, pp. 280-285
-
- Article
- Export citation
Achieving Uniform and Conformal ALD Coatings on Sub-10nm Pores Using Dual-Stage Exposure/ Purge at Optimized Growth Temperatures
-
- Journal:
- MRS Advances / Volume 3 / Issue 45-46 / 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 April 2018, pp. 2833-2839
- Print publication:
- 2018
-
- Article
- Export citation
Prevalence and composition of CHD at different altitudes in Tibet: a cross-sectional study
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 27 / Issue 8 / October 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 April 2017, pp. 1497-1503
-
- Article
- Export citation
Influence of different casting processes on high cycle fatigue behavior of Mg–10Gd–3Y–0.5Zr alloy
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 31 / Issue 16 / 29 August 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 June 2016, pp. 2538-2548
- Print publication:
- 29 August 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
Nitrogen fluorescence induced by the femtosecond intense laser pulses in air
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 4 / 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 March 2016, e7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Investigation on crack propagation in single crystal Ag with temperature dependence
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 30 / Issue 22 / 27 November 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 November 2015, pp. 3553-3563
- Print publication:
- 27 November 2015
-
- Article
- Export citation
The association between serum lipids and colorectal neoplasm: a systemic review and meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 18 / Issue 18 / December 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 March 2015, pp. 3355-3370
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Characterization of a novel spore wall protein NbSWP16 with proline-rich tandem repeats from Nosema bombycis (microsporidia)
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 142 / Issue 4 / April 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 November 2014, pp. 534-542
-
- Article
- Export citation
Expression of Urotensin II During Focal Cerebral Ischemic in Diabetic Rats
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 41 / Issue 4 / July 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 October 2014, pp. 498-503
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation