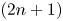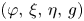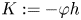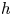191 results
On conformally flat minimal Legendrian submanifolds in the unit sphere
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 May 2024, pp. 1-30
-
- Article
- Export citation
Status and influencing factors of nurses’ burnout: A cross-sectional study during COVID-19 regular prevention and control in Jiangsu Province, China
-
- Journal:
- Cambridge Prisms: Global Mental Health / Volume 11 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2024, e54
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Longitudinal association between soft drink consumption and handgrip strength in adults: a prospective analysis from the Tianjin Chronic Low-Grade Systemic Inflammation and Health (TCLSIH) cohort study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2024, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
- Export citation
Association of the short-chain fatty acid levels and dietary quality with type 2 diabetes: a case–control study based on Henan Rural Cohort
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 10 / 28 May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 February 2024, pp. 1668-1677
- Print publication:
- 28 May 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Implementing a continuous quality-improvement framework for tuberculosis infection prevention and control in healthcare facilities in China, 2017–2019
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 45 / Issue 5 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2024, pp. 651-657
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Plasma Spectroscopy on Hydrogen-Carbon-Oxygen Foam Targets Driven by Laser-Generated Hohlraum Radiation
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Cross-Section Measurements of the 11B(p,α)2α Reaction near the First Resonant Energy
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Association between the PLTP rs4810479 SNP and Serum Lipid Traits in the Chinese Maonan and Han Populations
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2021 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e14
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A brief survey of observers for disturbance estimation and compensation
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Volunteers’ spiritual care competence and its relationship with attitudes toward palliative care: A cross-sectional study
-
- Journal:
- Palliative & Supportive Care , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 March 2023, pp. 1-7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
PD46 Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis In Healthcare: Scientometric And Bibliometric Analysis
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care / Volume 38 / Issue S1 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 December 2022, p. S107
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Added sugar intake and its forms and sources in relation to risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: results from the Tianjin Chronic Low-grade Systemic Inflammation and Health cohort study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 129 / Issue 12 / 28 June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 September 2022, pp. 2094-2101
- Print publication:
- 28 June 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Urban–rural disparities in the association between long-term exposure to high altitude and malnutrition among children under 5 years old: evidence from a cross-sectional study in Tibet
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 26 / Issue 4 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 September 2022, pp. 844-853
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Differences in associations between family functioning and anxious and depressive symptoms in Chinese women and their partners in early pregnancy
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 8 / Issue 5 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 August 2022, e158
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Role of dietary resistant starch in the regulation of broiler immunological characteristics
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 129 / Issue 4 / 28 February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 May 2022, pp. 617-626
- Print publication:
- 28 February 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Hydroclimatic changes in south-central China during the 4.2 ka event and their potential impacts on the development of Neolithic culture
-
- Journal:
- Quaternary Research / Volume 109 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 May 2022, pp. 39-52
-
- Article
- Export citation
Consolidating Product Lines via Mergers and Acquisitions: Evidence From the USPTO Trademark Data
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis / Volume 57 / Issue 8 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 March 2022, pp. 2968-2992
- Print publication:
- December 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Organ meat consumption and risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: the Tianjin Chronic Low-grade Systemic Inflammation and Health cohort study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 130 / Issue 2 / 28 July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2022, pp. 276-283
- Print publication:
- 28 July 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Drug resistance characteristics of Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates obtained between 2018 and 2020 in Sichuan, China
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 January 2022, e27
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation