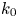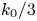25 results
An online method for ship trajectory compression using AIS data
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Navigation , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 May 2024, pp. 1-22
-
- Article
- Export citation
Alpha-Particle Generation from H-11B Fusion Initiated by Laser-Accelerated Boron Ions
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Gray matter atrophy is constrained by normal structural brain network architecture in depression
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 7 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2023, pp. 1318-1328
-
- Article
- Export citation
Tuber development and propagation are inhibited by GA3 effects on the DELLA-dependent pathway in purple nutsedge (Cyperus rotundus) – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 71 / Issue 5 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 November 2023, pp. 514-515
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Tuber development and propagation are inhibited by GA3 effects on the DELLA-dependent pathway in purple nutsedge (Cyperus rotundus)
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 71 / Issue 5 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 September 2023, pp. 453-461
-
- Article
- Export citation
Hydrodynamic instabilities of a dual-mode air–SF6 interface induced by a cylindrically convergent shock
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 963 / 25 May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 May 2023, A25
-
- Article
- Export citation
CYP4CJ6-mediated resistance to two neonicotinoid insecticides in Sitobion miscanthi (Takahashi)
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 112 / Issue 5 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2022, pp. 646-655
-
- Article
- Export citation
Evaluating the interactive effects of dietary habits and human gut microbiome on the risks of depression and anxiety
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 7 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2022, pp. 3047-3055
-
- Article
- Export citation
Progressive brain structural abnormality in depression assessed with MR imaging by using causal network analysis
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 5 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2021, pp. 2146-2155
-
- Article
- Export citation
Glucosamine use, smoking and risk of incident chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a large prospective cohort study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 128 / Issue 4 / 28 August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2021, pp. 721-732
- Print publication:
- 28 August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
FNDC5 polymorphism influences the association between sarcopenia and liver fibrosis in adults with biopsy-proven non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 126 / Issue 6 / 28 September 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 November 2020, pp. 813-824
- Print publication:
- 28 September 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Local dynamic spontaneous brain activity changes in first-episode, treatment-naïve patients with major depressive disorder and their associated gene expression profiles
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 52 / Issue 11 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 October 2020, pp. 2052-2061
-
- Article
- Export citation
Richtmyer–Meshkov instability on a dual-mode interface
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 905 / 25 December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 October 2020, A5
-
- Article
- Export citation
Evaluating the effect of birth weight on brain volumes and depression: An observational and genetic study using UK Biobank cohort
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 63 / Issue 1 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 July 2020, e73
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The southern Jiangsu coast is a critical moulting site for Spoon-billed Sandpiper Calidris pygmaea and Nordmann’s Greenshank Tringa guttifer
-
- Journal:
- Bird Conservation International / Volume 30 / Issue 4 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 May 2020, pp. 649-660
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Detection of Chlamydia psittaci and Chlamydia ibidis in the Endangered Crested Ibis (Nipponia nippon)
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 148 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2020, e1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Evolution of shock-accelerated heavy gas layer
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 886 / 10 March 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2020, A7
-
- Article
- Export citation
Interaction of a planar shock wave and a water droplet embedded with a vapour cavity
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 885 / 25 February 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 January 2020, R6
-
- Article
- Export citation
Persistent use of a shorebird staging site in the Yellow Sea despite severe declines in food resources implies a lack of alternatives
-
- Journal:
- Bird Conservation International / Volume 28 / Issue 4 / December 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 April 2018, pp. 534-548
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Fabrication of nitrogen doped carbon encapsulated ZnO particle and its application in a lithium ion conversion supercapacitor
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 32 / Issue 2 / 27 January 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 January 2017, pp. 334-342
- Print publication:
- 27 January 2017
-
- Article
- Export citation