116 results
A cluster of three extrapulmonary Mycobacterium abscessus infections linked to well-maintained water-based heater-cooler devices
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 45 / Issue 5 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 644-650
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
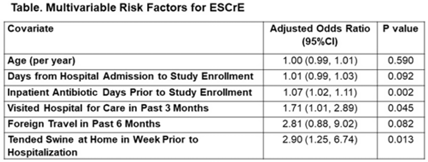
Colonization with extended-spectrum cephalosporin-resistant Enterobacterales (ESCrE) in hospitalized patients in Botswana
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, p. s81
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Relative uptake of organic and inorganic nitrogen by common weed species
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 71 / Issue 5 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 August 2023, pp. 470-477
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Medicalization of Madness in the Eighteenth Century - Bedlam in the New World: A Mexican Madhouse in the Age of Enlightenment. By Christina Ramos. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press, 2022. Pp. 266. $95.00 cloth; $34.95 paper; $26.99 e-book.
-
- Journal:
- The Americas / Volume 80 / Issue 2 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 April 2023, pp. 354-355
- Print publication:
- April 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Evaluation of a complex intervention for prisoners with common mental health problems, near to and after release: the Engager randomised controlled trial
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 222 / Issue 1 / January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 August 2022, pp. 18-26
- Print publication:
- January 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Application of single-cell transcriptomics to kinetoplastid research
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 148 / Issue 10 / September 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 March 2021, pp. 1223-1236
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Cryostratigraphy of mid-Miocene permafrost at Friis Hills, McMurdo Dry Valleys of Antarctica
-
- Journal:
- Antarctic Science / Volume 33 / Issue 2 / April 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 December 2020, pp. 174-188
-
- Article
- Export citation
Are cover crop mixtures better at suppressing weeds than cover crop monocultures?
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 68 / Issue 2 / March 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 January 2020, pp. 186-194
-
- Article
- Export citation
two - Dilemmas and conflicts in the legal system
-
-
- Book:
- Unaccompanied Young Migrants
- Published by:
- Bristol University Press
- Published online:
- 21 April 2022
- Print publication:
- 30 January 2019, pp 39-76
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Investigating tarps to facilitate organic no-till cabbage production with high-residue cover crops
-
- Journal:
- Renewable Agriculture and Food Systems / Volume 35 / Issue 3 / June 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 September 2018, pp. 227-233
-
- Article
- Export citation
Method of levels therapy for first-episode psychosis: rationale, design and baseline data for the feasibility randomised controlled Next Level study
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 4 / Issue 5 / September 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 August 2018, pp. 339-345
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The ablation zone in northeast Greenland: ice types, albedos and impurities
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology / Volume 56 / Issue 195 / 2010
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 September 2017, pp. 101-113
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
M. M. WINKLER , ARMINIUS THE LIBERATOR: MYTH AND IDEOLOGY. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2016. Pp. xxiv + 356, illus. isbn 9780190252915. £47.99.
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Roman Studies / Volume 107 / November 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 August 2017, pp. 440-441
- Print publication:
- November 2017
-
- Article
- Export citation
Environmental Correlates with Germinable Weed Seedbanks on Organic Farms across Northern New England
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 66 / Issue 1 / January 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 August 2017, pp. 78-93
-
- Article
- Export citation
Client Perceptions of Helpfulness in Therapy: a Novel Video-Rating Methodology for Examining Process Variables at Brief Intervals During a Single Session
-
- Journal:
- Behavioural and Cognitive Psychotherapy / Volume 45 / Issue 6 / November 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 May 2017, pp. 647-660
- Print publication:
- November 2017
-
- Article
- Export citation
Mode of Formation of “Ablation Hollows” Controlled by Dirt Content of Snow
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology / Volume 33 / Issue 114 / 1987
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 January 2017, pp. 135-139
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Solar-heating rates and temperature profiles in Antarctic snow and ice
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology / Volume 39 / Issue 131 / 1993
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 January 2017, pp. 99-110
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
A continuous multi-millennial record of surficial bivalve mollusk shells from the São Paulo Bight, Brazilian shelf
-
- Journal:
- Quaternary Research / Volume 81 / Issue 2 / March 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 January 2017, pp. 274-283
-
- Article
- Export citation
Cover-Crop Species as Distinct Biotic Filters in Weed Community Assembly
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 63 / Issue 1 / March 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 January 2017, pp. 282-295
-
- Article
- Export citation
Temperature measurements and heat transfer in near-surface snow at the South Pole
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology / Volume 43 / Issue 144 / 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 January 2017, pp. 339-351
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation