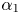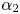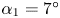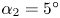67 results
THE INFLUENCE OF PLANT SPECIES AND PRETREATMENT ON THE 14C AGE OF CAREX-DOMINATED PEAT PLANTS OF A PEAT CORE FROM JINCHUAN MIRE, NE CHINA
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 December 2023, pp. 1-21
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Using molecular network analysis to understand current HIV-1 transmission characteristics in an inland area of Yunnan, China
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 July 2023, e124
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Separation length scaling for dual-incident shock wave–turbulent boundary layer interactions with different shock wave distances
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 960 / 10 April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 March 2023, A9
-
- Article
- Export citation
Cerebral blood flow changes and their genetic mechanisms in major depressive disorder: a combined neuroimaging and transcriptome study
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 14 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2023, pp. 6468-6480
-
- Article
- Export citation
Automatic taxonomic identification based on the Fossil Image Dataset (>415,000 images) and deep convolutional neural networks
-
- Journal:
- Paleobiology / Volume 49 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 June 2022, pp. 1-22
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
2 - Flooding Risk in the Lancang-Mekong River Basin under Global Change
- from Part I - Water-Related Risks under Climate Change
-
-
- Book:
- Climate Risk and Sustainable Water Management
- Published online:
- 17 March 2022
- Print publication:
- 07 April 2022, pp 29-46
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
An efficient high-power femtosecond laser based on periodic-layered-Kerr media nonlinear compression and a Yb:YAG regenerative amplifier
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 10 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 February 2022, e10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Metabolic Score for Visceral Fat: a novel predictor for the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 128 / Issue 6 / 28 September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 October 2021, pp. 1029-1036
- Print publication:
- 28 September 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Low selenium intake is associated with postpartum weight retention in Chinese women and impaired physical development of their offspring
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 126 / Issue 10 / 28 November 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2021, pp. 1498-1509
- Print publication:
- 28 November 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mental health services for infectious disease outbreaks including COVID-19: a rapid systematic review
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 50 / Issue 15 / November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 November 2020, pp. 2498-2513
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The descriptive epidemiology of coronavirus disease 2019 during the epidemic period in Lu'an, China: achieving limited community transmission using proactive response strategies
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 148 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 July 2020, e132
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Psychological impact of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) outbreak in health workers in China
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 148 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 May 2020, e96
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Evaluation Model for Hospital Response Capability for Public Health Emergency
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 15 / Issue 4 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 April 2020, pp. 403-408
-
- Article
- Export citation
High-power operation of double-pass pumped Nd:YVO4 thin disk laser
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 8 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 April 2020, e10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Precipitate phase transformation behavior, microstructure, and properties of Cu–Cr–Co–Si alloy
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 6 / 30 March 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 February 2020, pp. 623-632
- Print publication:
- 30 March 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Connexin 43 Knockdown Induces Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Affects Early Developmental Competence in Porcine Embryos
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 26 / Issue 2 / April 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 February 2020, pp. 287-296
- Print publication:
- April 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
A new tetraradial olivooid (Medusozoa) from the lower Cambrian (Stage 2) Yanjiahe Formation, South China
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Paleontology / Volume 94 / Issue 3 / May 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 December 2019, pp. 457-466
-
- Article
- Export citation