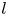351 results
On the probability of a Pareto record
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Probability in the Engineering and Informational Sciences , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 June 2024, pp. 1-13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
115 Strategies for Training and Advancing under-represented Researchers (STARs)
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue s1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 April 2024, p. 33
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
The Pandemic and Political Behavior: Staying the Course
-
- Journal:
- PS: Political Science & Politics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 January 2024, pp. 1-6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Extension event attendance increases adoption of weed management practices by sports field managers
-
- Journal:
- Weed Technology / Volume 37 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2023, pp. 578-587
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Agricultural Research Service Weed Science Research: Past, Present, and Future
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 71 / Issue 4 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 August 2023, pp. 312-327
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The age and paleoclimate implications of relict periglacial block deposits on the New England Tablelands, Australia
-
- Journal:
- Quaternary Research / Volume 111 / January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 August 2022, pp. 121-137
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Using laboratory intergroup conflict and riots as a “stress test”
-
- Journal:
- Behavioral and Brain Sciences / Volume 45 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 July 2022, e98
-
- Article
- Export citation
6 - Care arrangements for older adults: exploring the intergenerational contract in emigrant households of Goa, India
-
-
- Book:
- Care for Older Adults in India
- Published by:
- Bristol University Press
- Published online:
- 13 October 2022
- Print publication:
- 31 May 2022, pp 86-117
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Chapter 13 - Programs with Promise
- from Part III - Strategies for Inclusion and Retention
-
-
- Book:
- We're Not OK
- Published online:
- 21 April 2022
- Print publication:
- 05 May 2022, pp 218-232
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Automating 3D Imaging of Inorganic Nanoparticles
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 27 / Issue S1 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 July 2021, pp. 2864-2866
- Print publication:
- August 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Nomenclature for Pediatric and Congenital Cardiac Care: Unification of Clinical and Administrative Nomenclature – The 2021 International Paediatric and Congenital Cardiac Code (IPCCC) and the Eleventh Revision of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-11)
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 31 / Issue 7 / July 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 July 2021, pp. 1057-1188
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
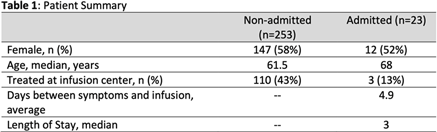
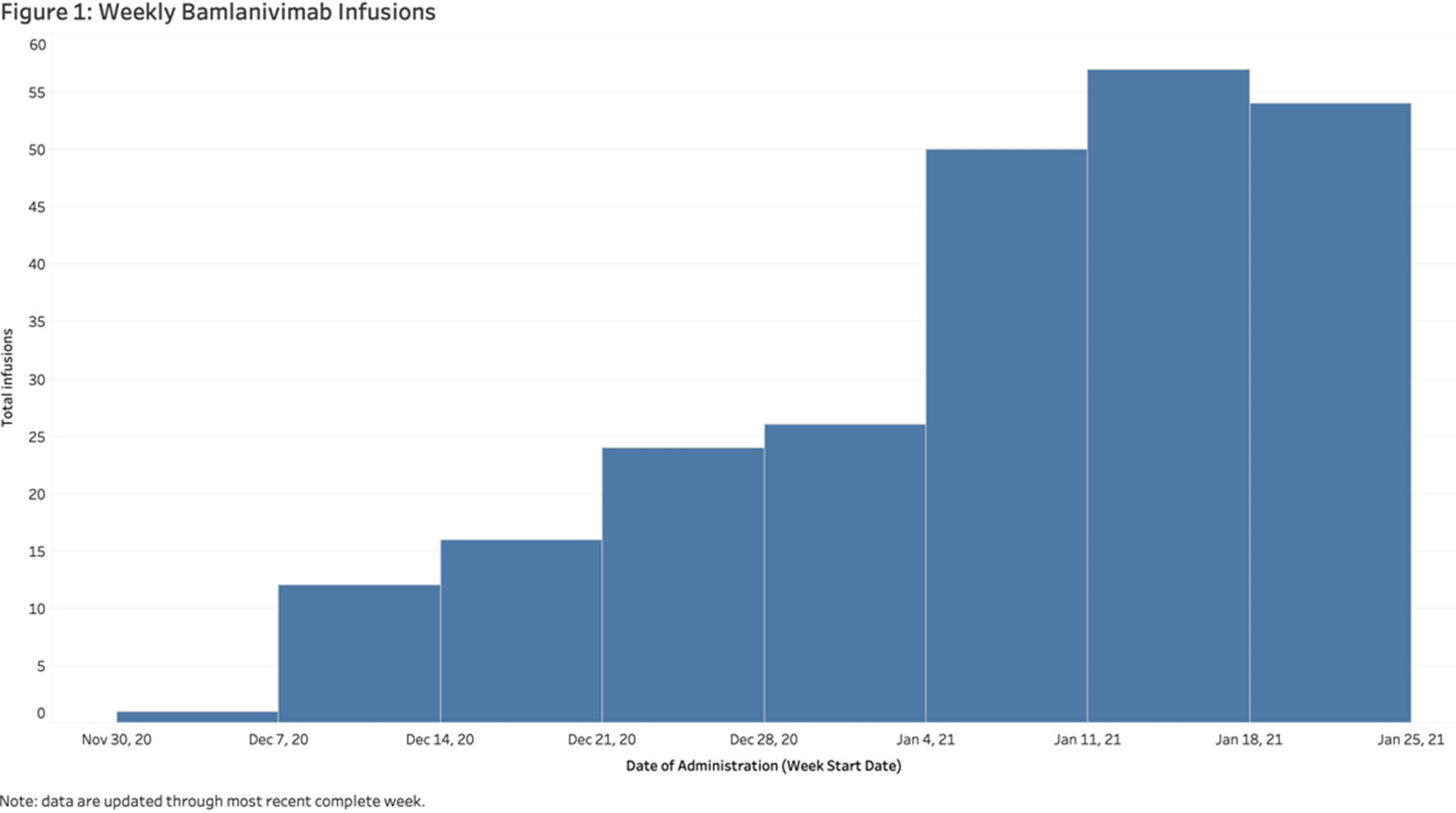
Antimicrobial Stewardship-Driven Monoclonal Antibody Treatment Program for COVID-19 Patients in the Bronx, New York
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 1 / Issue S1 / July 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 July 2021, p. s57
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
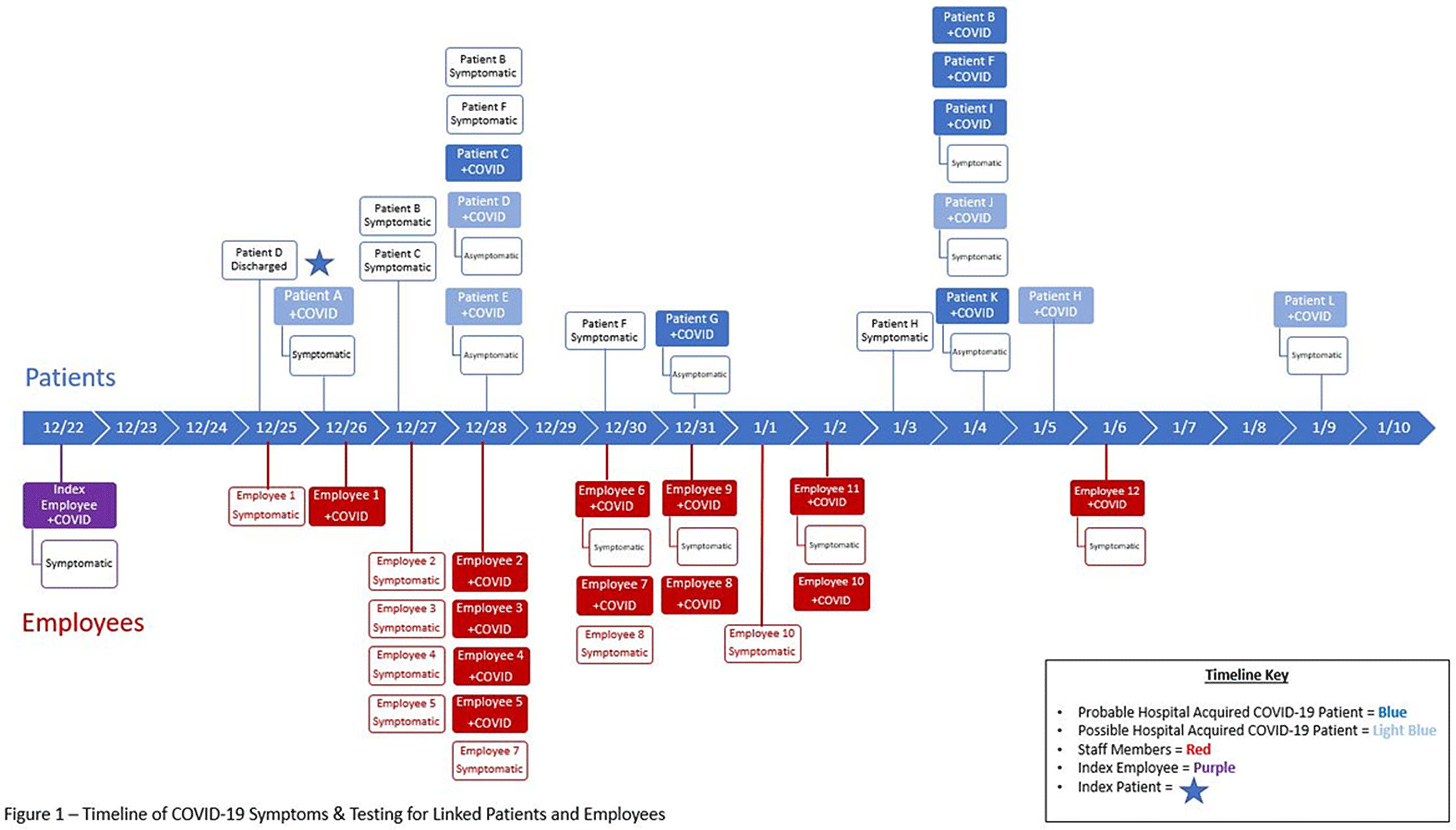
A Cluster of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Cases on an Inpatient Hospital Unit Involving Multiple Modes of Transmission
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 1 / Issue S1 / July 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 July 2021, pp. s2-s3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Effects of energy balance on appetite and physiological mediators of appetite during strenuous physical activity: secondary analysis of a randomised crossover trial
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 126 / Issue 10 / 28 November 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 January 2021, pp. 1571-1584
- Print publication:
- 28 November 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Big Data on BHR: Innovative Approaches to Analysing the Business & Human Rights Resource Centre Database – ERRATUM
-
- Journal:
- Business and Human Rights Journal / Volume 6 / Issue 1 / February 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 November 2020, p. 178
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Automorphy lifting for residually reducible
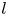 $l$-adic Galois representations, II
$l$-adic Galois representations, II
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Compositio Mathematica / Volume 156 / Issue 11 / November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 December 2020, pp. 2399-2422
- Print publication:
- November 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Big Data on BHR: Innovative Approaches to Analysing the Business & Human Rights Resource Centre Database
-
- Journal:
- Business and Human Rights Journal / Volume 6 / Issue 1 / February 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2020, pp. 120-126
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Breaking bivariate records
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Combinatorics, Probability and Computing / Volume 30 / Issue 1 / January 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 August 2020, pp. 105-123
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Fontan outcomes network: first steps towards building a lifespan registry for individuals with Fontan circulation in the United States – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 30 / Issue 9 / September 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 July 2020, p. 1381
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation