61 results
Do It Right the First Time? Exploring the First Cross-border Acquisition and Expansion Frequency of Emerging Market Multinationals
-
- Journal:
- Management and Organization Review , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 February 2024, pp. 1-27
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Coulomb-driven electroconvection turbulence in two-dimensional cavity
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 980 / 10 February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2024, A22
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Deep learning-based companion robot on senile dementia patients
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 28 / Issue S2 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, p. S3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Effects of monolaurin on intestinal barrier, blood biochemical profile, immunity and antioxidant function in porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus-infected piglets
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 2 / 28 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 August 2023, pp. 185-192
- Print publication:
- 28 January 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
SG-APSIC1170: Reduction of hospital-onset MRSA bacteremia with chlorhexidine baths among MRSA-colonized patients
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 March 2023, p. s19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Graph models for engineering design: Model encoding, and fidelity evaluation based on dataset and other sources of knowledge
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Calculation of collisionless pitch-angle scattering of runaway electrons with synchrotron radiation via high-order guiding-centre equation
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 88 / Issue 5 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 October 2022, 905880505
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Immunopathogenesis of patients with COVID-19: from the perspective of immune system ‘evolution’ and ‘revolution’
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine / Volume 24 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 April 2022, e19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Supplemental folic acid and/or multivitamins in pregnancy is associated with a decreased risk of childhood and adolescent nasopharyngeal carcinoma
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease / Volume 13 / Issue 5 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2021, pp. 550-555
-
- Article
- Export citation
Anisotropic Gauss curvature flows and their associated Dual Orlicz-Minkowski problems
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 152 / Issue 1 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 November 2021, pp. 148-162
- Print publication:
- February 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
In situ synthesis of zeolites by geopolymerization with NaOH/KOH mixed solution and their potential application for Cd(II) immobilization in paddy soil
-
- Journal:
- Clay Minerals / Volume 56 / Issue 2 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2021, pp. 156-167
-
- Article
- Export citation
Echinococcus granulosus cyst fluid suppresses inflammatory responses by inhibiting TRAF6 signalling in macrophages
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 148 / Issue 7 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 March 2021, pp. 887-894
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effects of Onabotulinum Toxin A on Gait in Parkinson’s Disease Patients with Foot Dystonia
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 49 / Issue 1 / January 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 March 2021, pp. 123-128
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dependence of fishbone cycle on energetic particle intensity in EAST low-magnetic-shear plasmas
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 86 / Issue 6 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 December 2020, 905860610
-
- Article
- Export citation
g-C3N4 nanoparticle@porous g-C3N4 composite photocatalytic materials with significantly enhanced photo-generated carrier separation efficiency
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 16 / 28 August 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 July 2020, pp. 2148-2157
- Print publication:
- 28 August 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
To alert coinfection of COVID-19 and dengue virus in developing countries in the dengue-endemic area
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 41 / Issue 12 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 May 2020, p. 1482
- Print publication:
- December 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The effects of geometry and heating rate on thermocapillary convection in the liquid bridge
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 881 / 25 December 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 October 2019, pp. 951-982
-
- Article
- Export citation
Thermodynamics of Complex Solids
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 19 / 14 October 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 October 2019, pp. 3241-3242
- Print publication:
- 14 October 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Recent advances in experimental thermodynamics of metal–organic frameworks
-
- Journal:
- Powder Diffraction / Volume 34 / Issue 4 / December 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2019, pp. 297-301
-
- Article
- Export citation


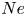
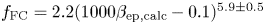
 ’ type curve. Based on this, we discuss the influence of heating rate on the oscillation mode. It is found that the heating rate affects the selection of critical mode, which results in a jump change of critical temperature difference. The findings of this study are helpful to better understand the critical modes and transition processes of thermocapillary convection in liquid bridges with different configurations.
’ type curve. Based on this, we discuss the influence of heating rate on the oscillation mode. It is found that the heating rate affects the selection of critical mode, which results in a jump change of critical temperature difference. The findings of this study are helpful to better understand the critical modes and transition processes of thermocapillary convection in liquid bridges with different configurations.